Posted on 03/04/2020
When building houses, people build on their own in order to save money. And due to the lack of professional skills and construction education, they cannot always take into account some important points on which the quality of not only the built house depends, but also the future life in him. For example, the choice of material depends on how warm and comfortable the house will be, and how much money will go for heating and maintenance. This important role in construction is played by the so-called "cold bridges". It is to them that today's HouseChief review will be devoted, in which we will consider what it is, what is the best way to build a house and what nuances are especially important.
Read in the article
- 1 What are cold bridges and how to identify them
- 2 The first "cold bridge" - wall material
- 3 Second "cold" bridge - masonry seams
- 4 Color value on the thermal imager screen
- 5 Cold bridge №3. Window and door lintels
What are cold bridges and how to identify them
The "cold bridge" is a section of the structure with low thermal resistance. It can be either vertical or horizontal. For example, walls and seams in masonry, windows, doors, roof and foundations. Quite a lot of heat can leave the house through such areas, and these losses due to cold bridges lead to a decrease in the comfort of housing, a noticeable decrease in the life of the house and, of course, an increase in payments for heating.
The first "cold bridge" - wall material
The question: what to build a house from is relevant for everyone, because the market for modern building materials is very wide. But everyone wants to live in a comfortable and warm home, especially in winter. And the preservation of heat in the house largely depends on what kind of wall material was chosen during the construction of the house, because up to 35% of the heat leaves through the walls. The thermal conductivity of the material is responsible for this indicator, the higher it is, the more heat the material passes through itself.
And for those who plan to build a "box" of the house, bring it under the roof, and live for some time in a house without exterior decoration - it is doubly important that the house is warm.
The table below shows for comparison the three main types of materials used in the arrangement of the walls of the house: wooden beams, aerated concrete blocks and expanded clay blocks. Physicomechanical characteristics are taken from materials manufacturers websites.
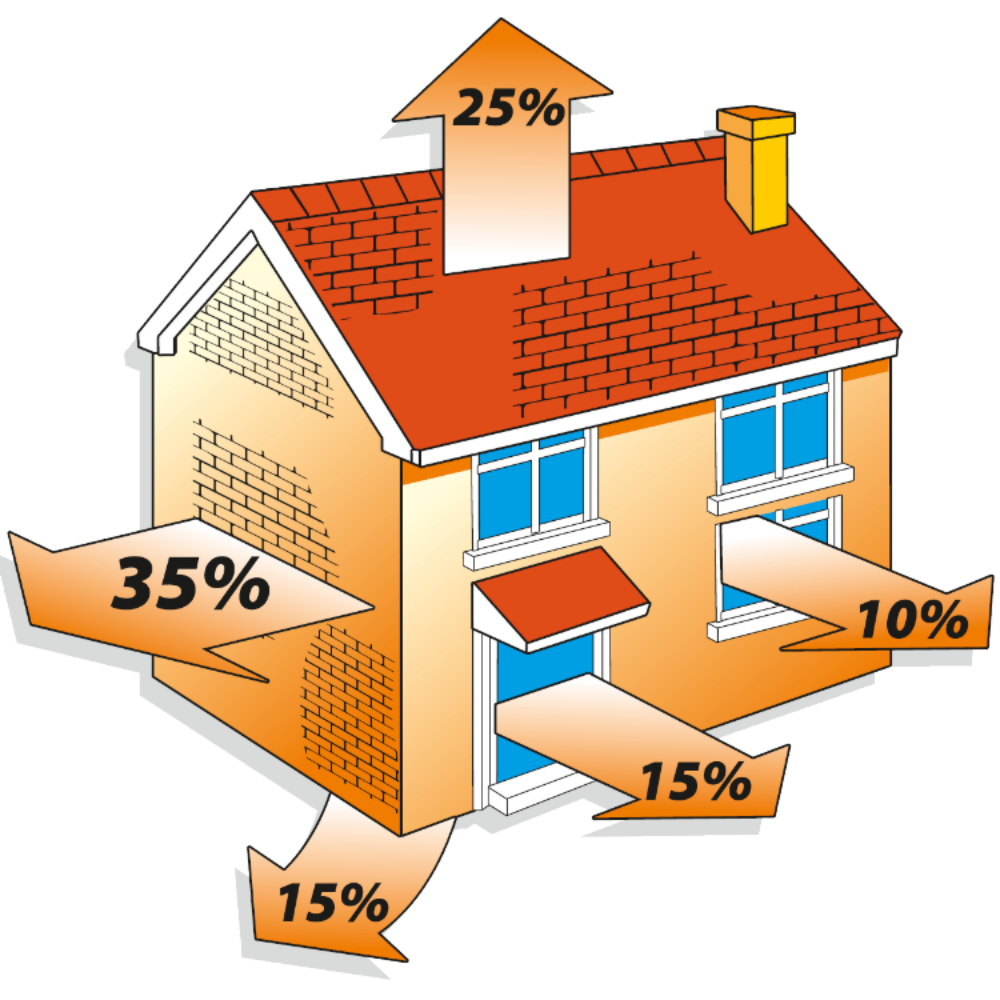
Table 1 - Thermal properties of various materials.
| Feature / Material | Density, kg / m³ | Thermal conductivity W / (m × C) | The maximum permissible wall thickness (for example, the south of the Tyumen region) R = 2.25 |
| Wooden beams | 540 and less | 0.15 (at a humidity of about 10%) | 200 mm block +30 mm. insulation R = 2.28 |
| Expanded clay block | 1 000 | 0.36 | (190 + 190 laying in two blocks) +50 mm. insulation R = 2.43 |
| Aerated concrete block | 500 | 0.11 | Block 400 mm. without insulation R = 3.00 |
As follows from the table, the warmest wall material is aerated concrete, which is best suited for permanent residence and may not require additional insulation. In second place is a wooden beam and in third place is an expanded clay block, which is one of the coldest building materials and requires mandatory additional thermal insulation.
Second "cold" bridge - masonry seams
As we saw in the diagram above, up to 35% of the total heat loss occurs through the walls and therefore it is necessary that the material from which they are laid and the masonry itself are of high quality. Why think about this during the construction planning phase? Yes, so as not to heat the street later and not to throw money down the drain.

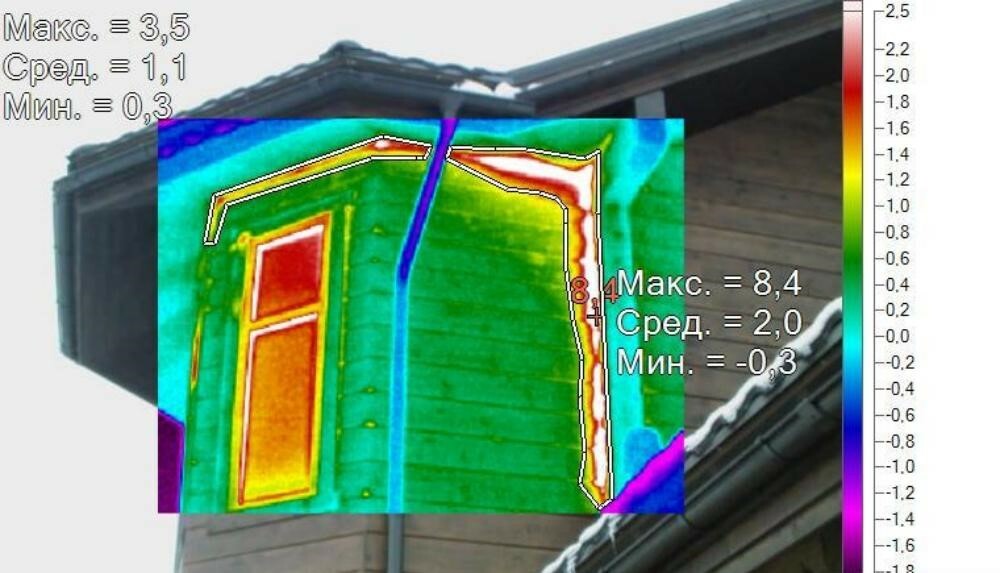
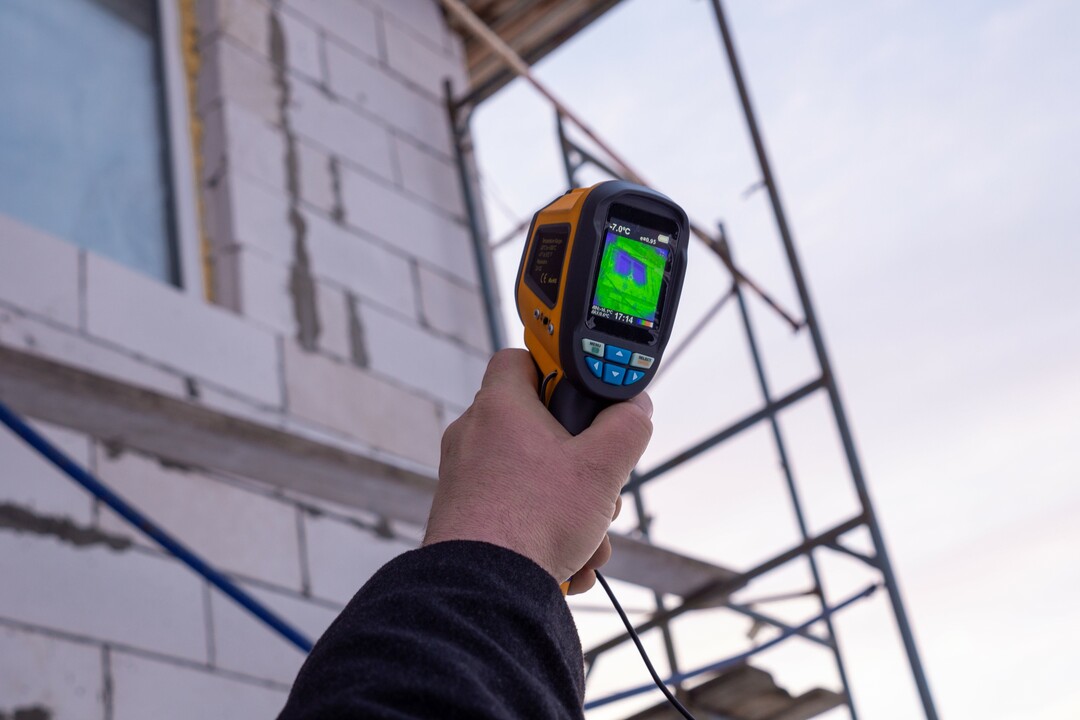
The thermal imager, which is a device for monitoring the temperature distribution on the surface of interest, helps to determine the heat loss in the building. A picture is displayed on the monitor of the device, on which a certain color corresponds to each temperature.
Color value on the thermal imager screen
When shooting heat loss is carried out from the street, then on the screen it is displayed as follows:
- Blue colour. Minimum heat loss designation;
- green. The average value of heat loss between the hottest place and the coldest place in the structure of the house;
- Red. This color indicates the maximum heat loss through the wall, windows or roof of the building.
When shooting a building from the inside, the color coding gets a different interpretation:
- blue. The greatest heat loss;
- green. Average value of heat losses in the building;
- Red. The minimum level of heat loss.
During the construction of a house from a wooden bar, it is required to insulate the joints with tow, jute, etc. If everything is done qualitatively, then the cold bridges will be minimal, and the walls and gaps between the rows of the timber will reliably keep the heat inside at home.
Claydite concrete is laid on a cement-sand mortar with a seam thickness of about 5-10 mm. Concrete conducts heat well and transfers it to the street just as well. He, in comparison with other materials, is the coldest, which means that it requires mandatory additional insulation. Therefore, only with the help of insulation and exterior decoration (siding, brick) can heat loss in the house be reduced.
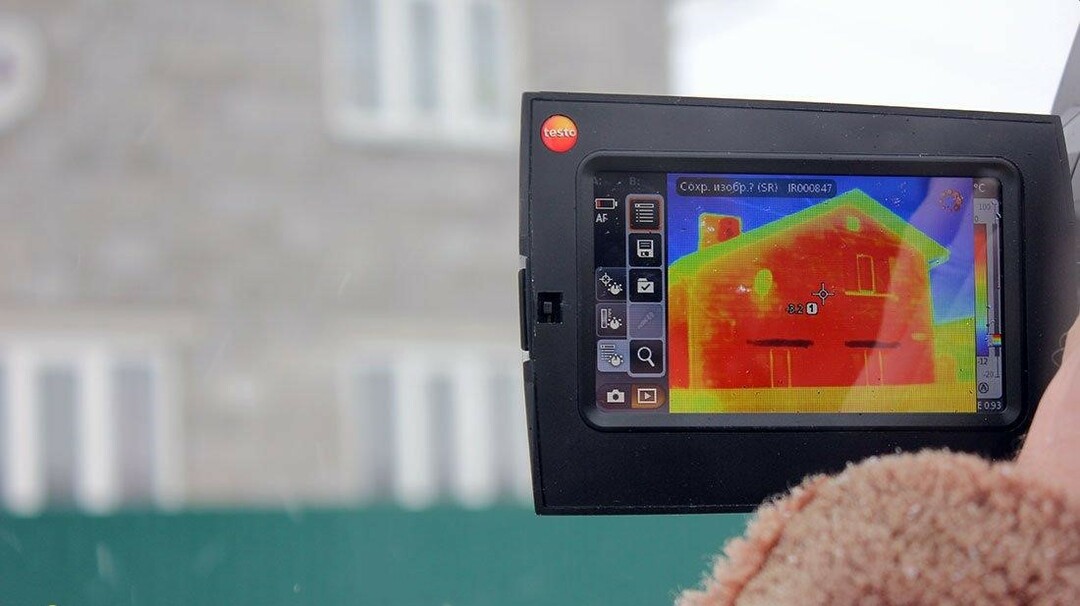

Aerated concrete is laid on mineral or polyurethane foam glue with a seam thickness of 1-3 mm. A homogeneous aerated concrete wall that does not have cold bridges is displayed in green on the monitor. That is, there is no heat loss through the walls. This means that the warmer the material and the fewer the masonry joints and their thickness, the warmer the wall surface. This is especially important for families who, for some reason, drove into an unfinished house, or began to live in a house without exterior decoration. In this case, a house made of aerated concrete will be comfortable for living.

Cold bridge №3. Window and door lintels
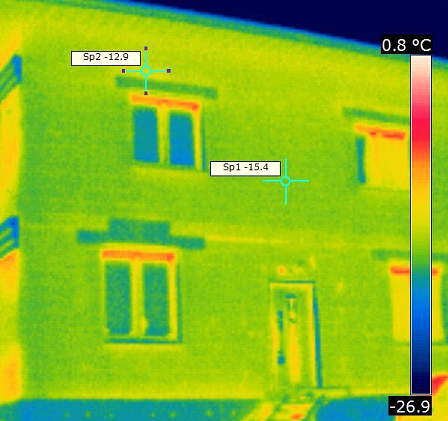
In total, doors and windows give up to 25% of the total heat from the house. In order to make it as warm as possible, along with the walls, lintels are also important, which are mounted over the place where windows and doors will be installed in the future.
In houses with expanded clay concrete walls, heavy reinforced concrete structures are used, which necessarily require additional external insulation, as, in principle, the house itself.

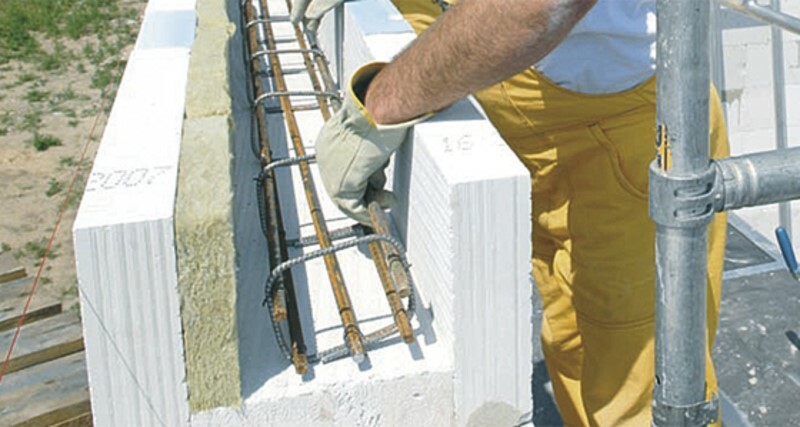
During the construction of buildings from aerated concrete blocks, special U-blocks are used, which are used specifically to create a window or door lintel. However, they also need additional thermal insulation. As a rule, insulating material is inserted into the inside of the block and after that it is poured with a fastening solution.

So, we see, in the first place is a house built from a bar due to the absence of jumpers in the structure in principle. On the second - houses made of aerated concrete with the possibility of using U-shaped blocks together with insulation in the construction, which protect the lintel zones from hypothermia. And on the third - houses made of expanded clay blocks, during the construction of which reinforced concrete lintels are used, which are cold due to the large amount of concrete in the composition.
Let's summarize.
Table 2 - The best material for building a house.
Feature /Material | Beams | Expanded clay block | Gas block |
| Density, kg / m3 Thermal conductivity W / (m * C) | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| Cold bridges - masonry seams | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| Cold bridges - lintels | 1 | 3 | 2 |
Points, 1 - leader, 3 - outsider.
As a result, the first place in terms of characteristics is aerated concrete blockbeing the warmest material. A house made of this material, subject to all technologies, will be the most energy-efficient. In the second position of the building from wooden beam, which is also a good option. Expanded clay block, despite its popularity, was at the bottom of the rating, since it is the coldest building material that requires mandatory insulation.



