Since the establishment of the first USB specification, the technology could significantly change the world and the connected peripherals to simplify the user's handling of the personal computer. USB success is easy to explain - a variety of cables replaced by one common connector for different types of devices, without loss of signal quality and bit rate. Now USB - Main way to connect smart phones, printers, external storage devices and many other devices to a PC or to each other. Now we shall understand in cables for cell types and USB form factors.
Read article
- 1 types of connectors
- 2 Cable colors USB-cable
- 2.1 The colors in the USB 2.0
- 2.2 The colors in the USB 3.0
- 3 USB on motherboards
types of connectors
Apparently, manufacturers are trying to confuse users as much as possible a whole range of different form factors and their modifications. Moreover, the algorithms which work interfaces are constantly improved, changed and supplemented. It is worth more to deal with all this. There is a concept of form factor and BOM version. Form Factor - this connector form, that is how it looks externally. They can be designated types «A», «B», «C». The first two have their own micro and mini-version.
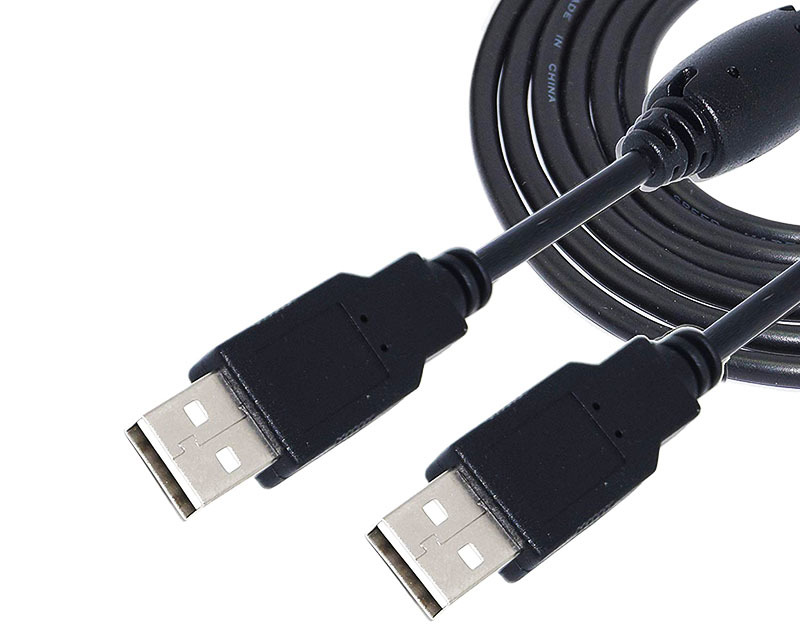

PHOTO: images-na.ssl-images-amazon.com
Regulation states that the type "A" is intended for connection to the controller or hub, that is, to a PC, and the type «B» - to the periphery. Any modern laptop or desktop PC necessarily have on board at least one USB connector is a conventional type «A». And, for example, printers, equipped connector type «B». «B» from the small versions of connectors most accustomed version of micro and mini type.

PHOTO: countrysale.ru
They are most commonly used in smartphones and external hard drives. «B» mini occur more rarely, but the micro is still relevant. It can be found even in the most recent versions of mobile phones. But it may soon displace the more promising type «C». In general, a standard USB type "A" - a standard rectangular connector with 4 pins on a laptop or PC, the usual type of 'Bed and' - more "square" connector, found at the printers. Micro-USB type «B» - a small 5-pin connector, which serves for charging and data transfer on mobile phones.
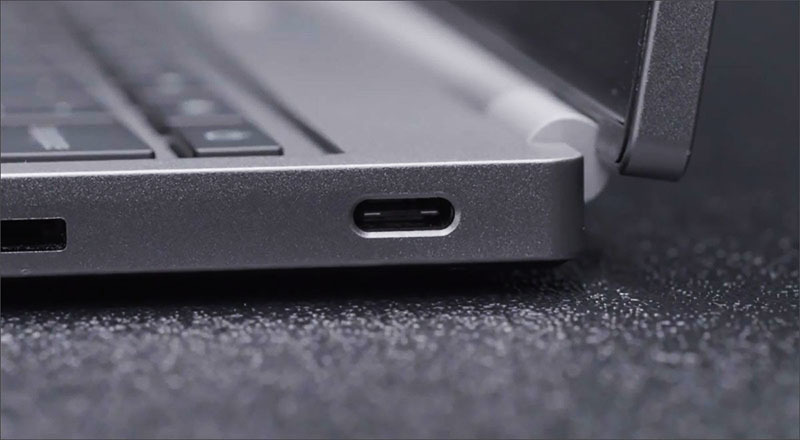

PHOTO: vladtime.ru
Specification USB «C» type was first published in August 2014. Despite this, the device began to be supplied with this connector is relatively recent. Standard finally become symmetrical, that is, to insert the plug into the socket can be any party. Moreover, it can operate in alternate modes - DisplayPort, HDMI and Thunderbolt connecting respective adapters.
Specifications confuse users, no less. The number specified after the abbreviation USB - and there are versions of the specification designation. In fact, the specification - is a set of algorithms, rules and instructions for developers who need to use them in the manufacture of devices and cables. Current date version - 3.2. With the next specification to add new features, and increased data transfer rate. For example, the first - the rate was 1.0 to 1.5 Mbit / s and 2 × 3.2 Generation 2 - up to 20 Gbit / s. Eye type specification can be determined by the color of the connector. Blue - 3.0 and above, black - 2.0, gray or white - 1.0. Also, the "A" type connectors 3.0 and higher 9-pin, whereas 2.0 and below - 4. The special relationship between the connector type and specification, but there are small features. For example, a common type "A" and «B» can be used all kinds of specifications - from 1.0 to 3.2. Here are just among the connector type "A" revision 3.0 and later versions are no micro and mini.
Cable colors USB-cable
cable pinout should be considered in the context of the specifications. So how much does not matter the form-factor and small changes are reflected in the specification itself, we consider the version 2.0 and 3.0.
The colors in the USB 2.0
Conventional types of «A» and «B» have 4 contact. Traditionally, data transmission uses two of them, denoted generally «D +» and «D-». Inside are green, white or gold color. For power supply uses a red or orange wire. "Land" is usually a blue or black.
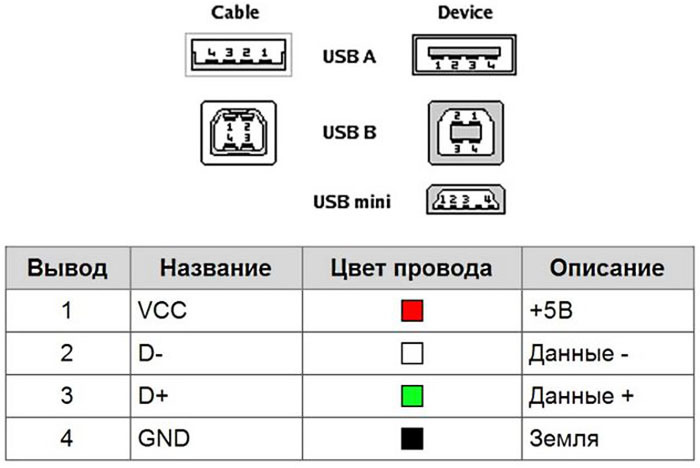
PHOTO: mastervintik.ru
Colors in micro or mini versions often do not change. However, they present a fifth contact which determines which is connected as a device - the host or peripherals. Physically wire is absent, there is a contact, which, depending on the type "A" or «B», or connected to "ground" or not.
The colors in the USB 3.0
USB 3.0 describes the three types of USB - «A», «B» and «C». The first two have a 9-pin and the same color scheme. 4 contacts have come from USB 2.0, have the same coloring: food - red, data - white and green, "earth" - black. There is also another "land"
not having colors using a metal wire. High speed data transfer is carried out 4 wires - two for reception, two for transmitting. Usually, they are painted in yellow, blue, purple and orange. In versions of «B» micro has an additional contact which, by analogy with 2.0, indicates the type of connection the host peripherals.
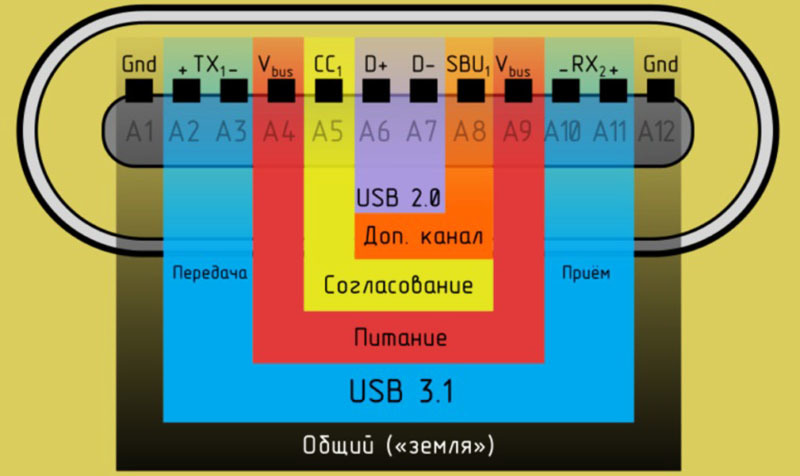
PHOTO: droidov.com
USB 3.1 for «C» 24 regulates type contact 12 on each side, than, in fact, achieved reflectivity interface. In the center of the connector two pins 6 and 7 come from USB 2.0 - is the transmission and reception of data, they are indicated by white and green. They exist for compatibility with older devices. Contact №5 configuration. It is necessary to determine the connection state (off), it also calculates required to perform current and voltage of the device. Eighth contact - supplemental channel used in rare cases to transfer a data type, such as sound. Contacts 4 and 9 - Power lines are indicated in the same way as in 2.0 - red. Pins 2, 3, 10 and 11 - this is USB 3.1. This data channels at high speed. The colors are not set tough standards, so they can be arbitrary. Along the edges, on pins 1, 12 are "earth".
USB on motherboards
Going a bit further into electronics, then directly to the PC USB-devices connected via USB-controller that can part of the computer system logic or be as a separate chip working with memory directly, bypassing the central processor. The motherboard connector is a set of connectors for output to the front or back of the computer. Wire end or separate chips, connectors, or unit designed for one or two external connector. USB 2.0 on board has 9 pins, and 3.0 and above - 19. For connections can not be active at all. If you pay attention, the pins are divided into two lines - 5 and 4 each for USB 2.0. Fifth contact in front of an empty place - a kind of key. It has no purpose, but it can be guided by knowing the rest of the designation of contacts. They are, incidentally come in pairs. That is, immediately after the "empty" contact pair goes "ground", then the data «D +» and data «D-», at the end of - the power.
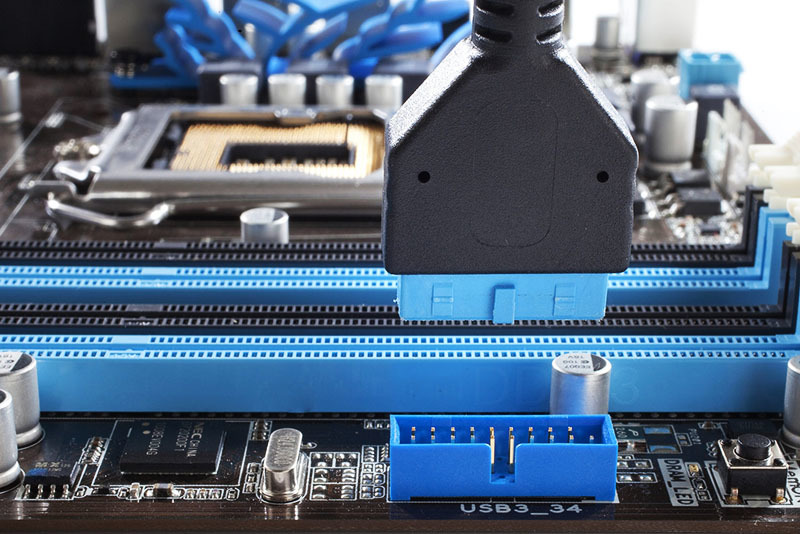
PHOTO: computerbase.de
The USB 3.0 logic contacts placement has changed a bit, although they also come in pairs. But remember them makes no sense, since the cable from the motherboard to the external USB terminals usually has a fixed size, so stick it will not work properly.
Harmonization of standards and connectors to connect the various devices should lead to a single result - all peripherals and external devices to be connected via the same interface and cable. Due to this, in the future it will disappear like graduations, house mushrooming mass of incompatible cables and chargers. This is in fact the truth is both more convenient and more economical.



