If building a house more often trust professionals, then various extensions, the need for which arises during operation, are often erected with their own hands. The most difficult unit in combining such structures is the place where the roof adjoins to the main structure. In this article, we will tell you how to dock the roof of an extension and a house in various design options: single-slope, gable, broken. And as well as how to dock the roofs of the main and attached structures.
Read in the article
- 1 Shed roof of an extension to the house
- 2 Extension to a house with a gable roof
- 3 Annex building with hip (gable, sloping) roof
- 4 Technologies for joining the roof of the extension and the house
- 4.1 Plank (rail) abutment
- 4.2 Flashing
- 5 Docking the roof of the extension and the roof of the house
- 6 Summing up
Shed roof of an extension to the house
The most economical and simple structure of the roof of the extension is one-pitched. As a rule, it is connected to the wall of the main structure by a knot with a longitudinal abutment. At the same time, it is not recommended to make a rigid connection between the roof structure of the extension and the wall of the house. The reason lies in the use of unrelated foundations. In the extension, it is usually columnar. Uneven shrinkage of both structures is guaranteed to cause destruction of the rigid connection between them.
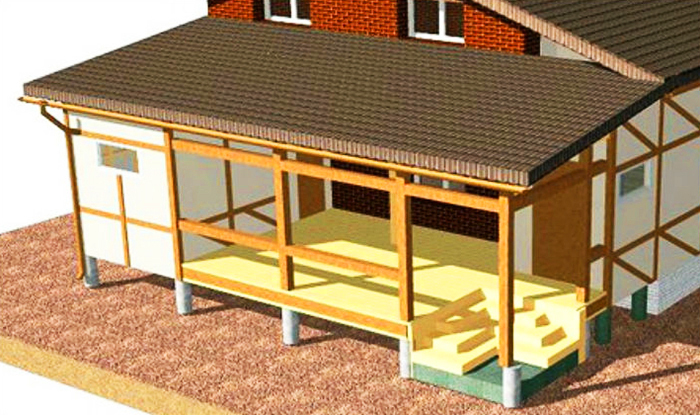

Attaching the rafter system of the extension to the house can be done in two ways, depending on the positioning.

Through a sliding connection with a longitudinal groove or a shrinkage compensator device - provides reliable fixing to the wall and at the same time prevents the formation of cracks in case of uneven shrinkage.
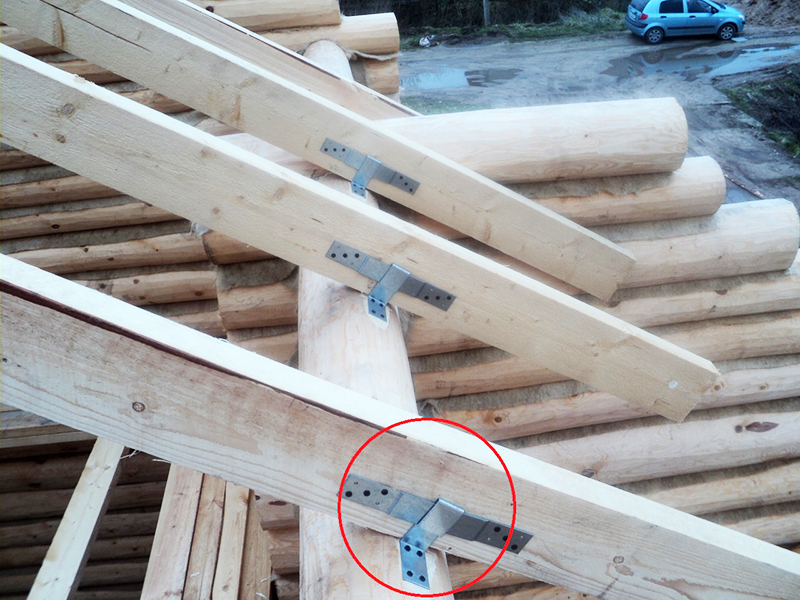 PHOTO: all-for-remont.ru
PHOTO: all-for-remont.ruThe greatest problems arise in the nodal structures for connecting the roofing pie of the extension to the wall. In such joints, gutters or aprons made of galvanized sheet are provided for water drainage.
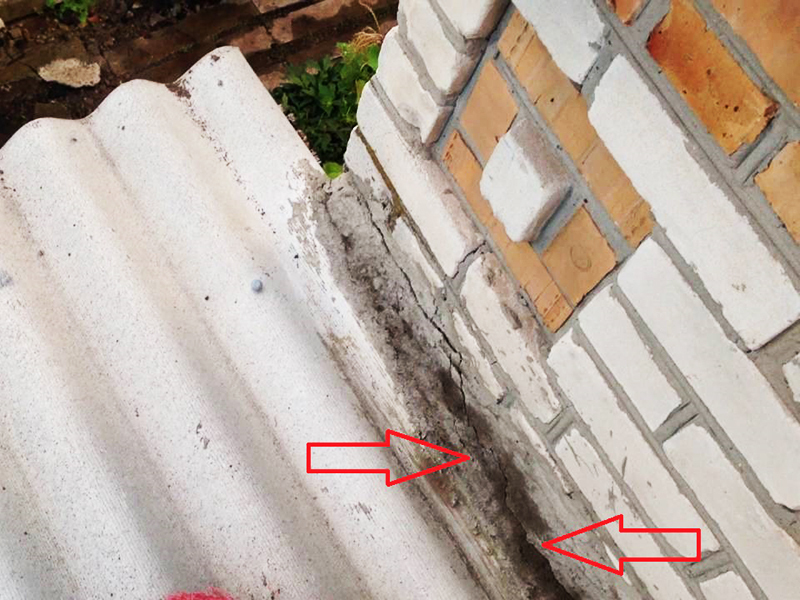 PHOTO: i.ytimg.com
PHOTO: i.ytimg.comIf possible, the roof of the extension should be installed under the roof of the main house. The slope angle must be at least 10º. The material of both roofs should be the same or at least comparable in color and texture.
It should be noted that the attached premises are, as a rule, below the main building. Consequently, water will drain onto their roof, and snow will fall from the main roof. Therefore, the issues of strength and waterproofing must be given top priority. The connection to the main building is made through an embedded beam.
Extension to a house with a gable roof
This option is used for outbuildings, which will later be used as full-fledged premises of the main structure. As a rule, the extension itself is performed on massive foundationconnected to the load-bearing base of the house. The walls are also connected using embedded elements.
 PHOTO: m-strana.ru
PHOTO: m-strana.ruThe gable rafter structure provides for an attic. The materials used are solid wood or glued beams. For rolling, a section of 150 × 100 mm is used, for a rafter system - 100 × 100 mm². The installation pitch of load-bearing elements is not more than 700 mm, and when using insulation - 600 mm.
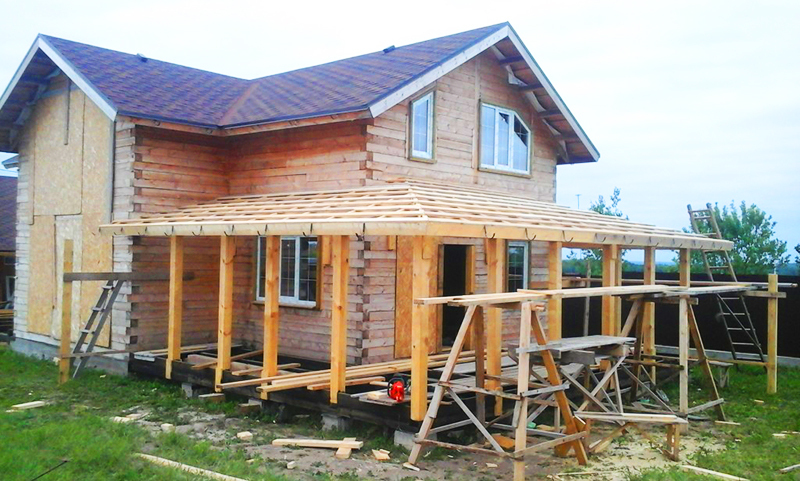 PHOTO: strindustry.ru
PHOTO: strindustry.ruThe connection of the gable roof of the extension to the main building is done through flashing or inset.
Annex building with hip (gable, sloping) roof
Roofs on annexes with a multifaceted or non-linear shape are highly complex. But, as a rule, this refers to the structural performance of the rafter system. And in the places adjacent to the main building, standard technologies are used for sealing joints, using embedded elements or anchor beams (rails).
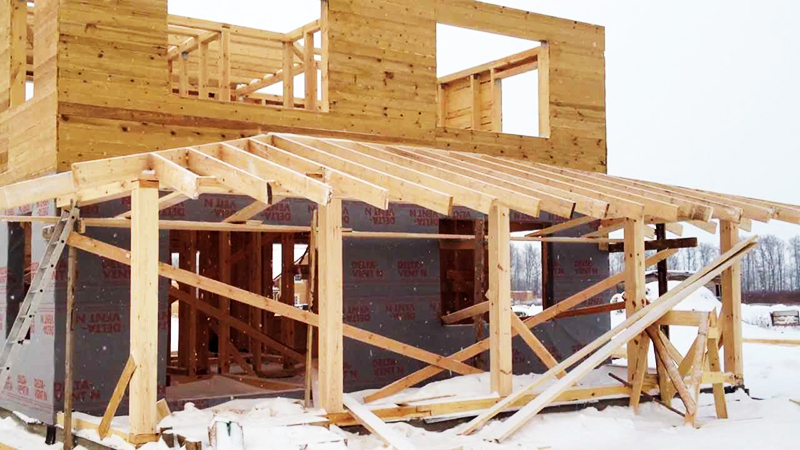 PHOTO: strindustry.ru
PHOTO: strindustry.ruThe only difference is the shape of the contact line. It is rarely linear, more often it consists of several segments directed at an angle. In this case, to maintain tightness, aprons are used - small self-supporting canopies made of galvanized sheet, fixed to the wall with dowels or screws, depending on the material of construction at home.
 PHOTO: strindustry.ru
PHOTO: strindustry.ruTechnologies for joining the roof of the extension and the house
Fitting points of roof elements of various types of building structures, for example, extensions, canopies, awnings, chimneys, ventilation and roof windows are exposed to more intense loads than the standard roof. The reason is the accumulation of branches, leaves and other debris at the junction. In winter there snow accumulates, and when it rains, the main water streams descend on some of these structures.
Plank (rail) abutment
This method is recommended for a combination of the following factors:
- the wall of the house has no embedded parts;
- the extension is not rigidly connected to the main building, and the shrinkage will occur unevenly;
- the roof slope of the extension is located at an angle of more than 5º;
- used as a roofing material metal tile, metal profiles, asbestos slate or shingles, etc.
The best way to seal the joint is to use an external apron with additional fastening through a wooden strip.
Important! This method is not recommended for use if the walls of the structure are made of concrete panels, since gating significantly weakens such a structure.
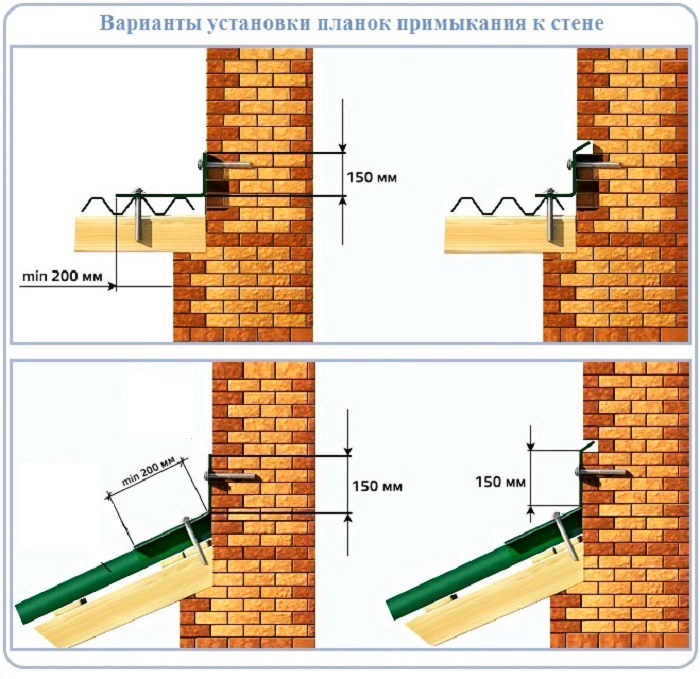 PHOTO: stroitel-kom.zp.ua
PHOTO: stroitel-kom.zp.ua| Illustration | Description of action |
 PHOTO: stroitel-kom.zp.ua PHOTO: stroitel-kom.zp.ua | We mark on the wall the height of the feigned plank |
 PHOTO: stroitel-kom.zp.ua PHOTO: stroitel-kom.zp.ua | Choosing a grinder strobe |
 PHOTO: stroitel-kom.zp.ua PHOTO: stroitel-kom.zp.ua | Thoroughly clean the strobe from dust |
 PHOTO: stroitel-kom.zp.ua PHOTO: stroitel-kom.zp.ua | We set a bar in the gate |
 PHOTO: stroitel-kom.zp.ua PHOTO: stroitel-kom.zp.ua | Sealing with silicone sealant |
Flashing
The joint is sealed using various primers, sealants, mastics and roll insulating materials. Used in the following cases:
- soft or roll roofing is used as a roofing material;
- the roof slope has an angle of less than 5º;
- no damage to the wall is allowed.
The application of sealants is carried out with a brush or roller, and as a reinforcing material, roofing material is used without powders or geotextile. Preparatory work consists of standard processes:
- the wall surface is cleaned of dirt, remnants of old sealing materials;
- if rolled roofing material with powder is used, then it is removed in the area adjacent to the wall. The sealant will be applied there;
- polymer-based roofing membranes are degreased;
- wall material (concrete, brick, OSB) is treated with a deep penetration primer to normalize moisture absorption.
| Illustration | Description of action |
 PHOTO: YouTube.com PHOTO: YouTube.com | The mastic is applied to the prepared area with a brush or roller. |
 PHOTO: YouTube.com PHOTO: YouTube.com | A strip of geotextile with a width of at least 50 cm is laid on top of the mastic: 25 cm each on the wall and roof. Laying is carried out immediately after processing the structure with a sealant so that the roll material adheres to the base |
 PHOTO: YouTube.com PHOTO: YouTube.com | A layer of mastic is again laid on the geotextile. Application is carried out after complete drying of the previous layer covered with geotextile. Depending on from the type of sealant (mastic), the technological pause period can be from several hours to half a day |
If desired, you can apply another layer of mastic, painted in the color of the roofing, to the surface of the elements to be connected.
Docking the roof of the extension and the roof of the house
Splicing the roofs of the main building with an extension is the most reliable way to protect the structure from leaks. For this, the extension must have a solid base that does not lend itself to shrinkage. As a rule, it is tape or a slab foundation that is an extension of the structural foundation of the main building. Also, the walls of the extension are connected to the walls of the main structure using anchors. This is how the extension and the building are combined into a single structure. Roof docking is the most time consuming and costly process, requiring partial dismantling of the roof of the main building.
When the rafter frame of the extension is ready, you can dock it to the roof of the house, connecting it into a single whole.
 PHOTO: YouTube.com
PHOTO: YouTube.com| Illustration | Description of action |
 PHOTO: YouTube.com PHOTO: YouTube.com | We lengthen the ridge of the garage roof. To do this, we use a beam of the same section as the ridge. We extend it until it rests against the plane of the roof of the house |
 PHOTO: YouTube.com PHOTO: YouTube.com | Mark the cutting lines near the ridge and slope |
 PHOTO: YouTube.com PHOTO: YouTube.com | Fasten with nails and screws in the indicated places |
 PHOTO: YouTube.com PHOTO: YouTube.com | Using a colored cord on both sides of the ridge, mark the line where the valley will pass |
 PHOTO: YouTube.com PHOTO: YouTube.com | We nail down two boards on which additional rafters will rest |
 PHOTO: YouTube.com PHOTO: YouTube.com | We make a rafter template: 1 - the angle of the roof slope, 2 - the right angle of the heel resting on the ridge |
 PHOTO: YouTube.com PHOTO: YouTube.com | We measure the length of the rafters from the ridge to the support board |
 PHOTO: YouTube.com PHOTO: YouTube.com | Using the template, mark the required corners and cut the rafters |
 PHOTO: YouTube.com PHOTO: YouTube.com | It should be remembered that when trimming a rafter resting on a roof slope, the tilt angle of the saw must be set to a value corresponding to the slope angle of the main roof |
 PHOTO: YouTube.com PHOTO: YouTube.com | All additional rafters are cut and fastened in the same way. |
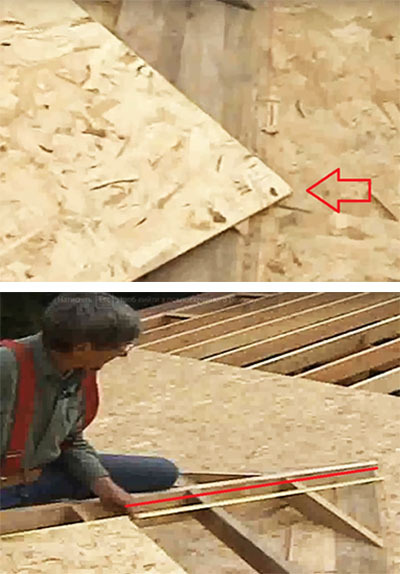 PHOTO: YouTube.com PHOTO: YouTube.com | We lay the OSB sheet on the rafters and move it so that the corner rests against the slope of the roof of the house. Then we measure the distance along the ridge of the garage roof from the house to the edge of the sheet |
 PHOTO: YouTube.com PHOTO: YouTube.com | We transfer the size to the sheet, measuring it from the angle set on the slope of the house. Then we connect the resulting point and the angle on the skate and cut |
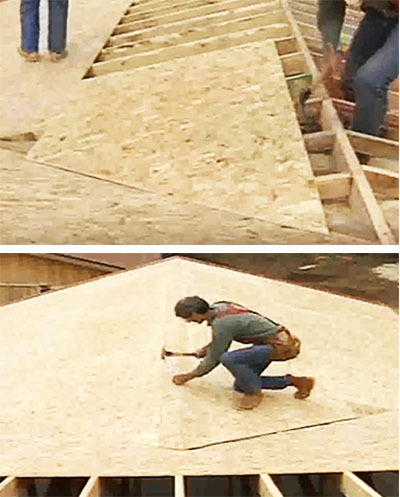 PHOTO: YouTube.com PHOTO: YouTube.com | We fix the sheet, we do the same operation with another slope |
The two roofs are connected into one structure and are ready for the installation of the roofing material. The joint is protected by a standard valley.
For more information about connecting the roofing structures of the house and the extension, see the video:
Summing up
The article presented three main technologies for connecting the roof of the extension to the building. They differ significantly in cost, complexity of execution and labor intensity. However, these designs are not interchangeable. Each of them has its own specific area of application.
- The abutment rail is used if the extension has a weak foundation and will be subject to more intense shrinkage. These can be covered terraces or summer verandas with roofs that have a large slope.
- Flashing - is used if the extension is more rigidly connected to the house, and also has a small roof slope angle. These are garages, workshops, winter gardens and capital verandas.
- Docking (splicing) roofs. It is used if the attached part, in fact, by its design and purpose, will be part of the house itself.
If the information provided in the article is useful to you, recommend it to your friends, leave a review and take part in the discussion.
