CONTENT
- 1 SSD solid state drive - what is it
- 2 What is an SSD drive in a computer for?
- 3 SSD hard drive device of laptop and in computer
- 4 How an SSD works
- 5 Types of hard drives
- 6 General characteristics of SSD (Solid State Disk)
- 7 Leading manufacturers of SSD drives for PC
- 8 Which SSD drive is better to buy
- 9 Answers to frequently asked questions about SSD
SSD solid state drive - what is it
SSD stands for Solid-State Drive. That, in fact, is translated - solid state drive. Its peculiarity lies in the fact that it does not contain moving mechanical parts: inside there are only boards and microcircuits, with the help of which information is recorded, stored and read.
The history of the SSD began a long time ago. For the first time, some kind of similarity was able to implement StorageTek in 1985. But at that time, the high cost and low manufacturability of components did not allow the massive introduction of solutions to the masses, yes and there was no particular answer why a fast SSD drive is needed in a computer, if the interfaces and peripherals still worked slowly. But in the early 2010s, the popularity of SSDs increased dramatically. Almost every new laptop now comes with either an SSD or a hybrid hard drive configuration. Next, we will look at what it is - an SSD in a laptop or desktop computer.
What is an SSD drive in a computer for?
SSDs are no different from HDDs in terms of their purpose. It is designed to perform the same function - to store data, operating system, paging files, and the like. Naturally, this replacement is more expensive in terms of gigabytes / ruble. It is more than likely that the situation will change in the near future.
SSD hard drive device of laptop and in computer
There is essentially no difference between what an SSD is in a laptop and a desktop computer. Externally, the device can be a case similar to an HDD, or it can be made as a board for installation in a type M connector. 2. If you disassemble the SSD or look at the board, then it is very similar in design to an ordinary USB flash drive. In general, an SSD is a large flash drive, with the same principle of operation.
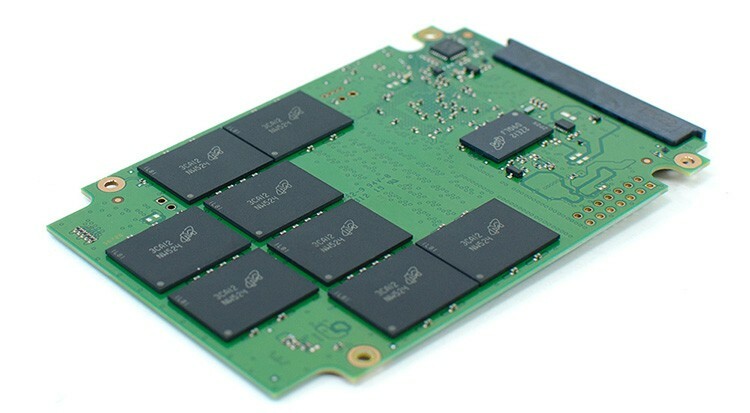

The controller manages the entire device, which distributes data to cells, monitors their status, deletion and, in general, performs all functions similar to the functions of a processor in a computer.
The memory itself is flash memory, the same as on flash drives. The SSD uses the NAND type, which is a three-dimensional arrangement of conductors where a series of cells are used at the intersections.

According to the method of writing data into a cell, two types of implementation are distinguished: SLC - Single-level Cell and MLC - Multi-level Cell. As you might guess, in the first case only one bit is written in one cell, in the second - several. Now another type has emerged from the MLC, the name of which has become established in everyday life, although it is included in a subset of this type - TLC, Triple-level Cell.
There are a number of advantages and disadvantages to each implementation. MLC comes out cheaper in terms of volume / price ratio. This makes the SSD hard drive cheaper in the long run, which affects consumer choice as well. But the structure of recording in several layers imposes restrictions on the number of write cycles and performance. The more nesting levels are used, the more complex the algorithm for working with cells becomes and the less resource. SLC is proportionally more expensive, has a greater resource and performance.
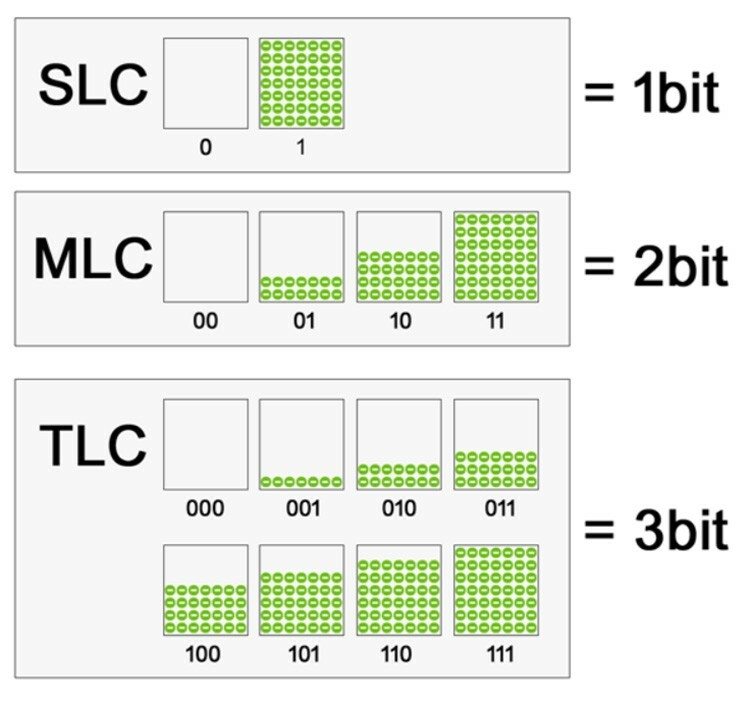
Manufacturers solve problems with the resource and reliability of memory using algorithms that allow control the process of using cells: recording is made to those parts of memory that were used least of all. Another approach is also used - memory reservation. Almost every SSD reserves about 20% of the memory in order to replenish it from there in case of loss of a cell.
How an SSD works
Probably, many people know how a regular hard disk works - a magnetic head runs from the beginning to the edge of a rotating disk and reads data from the tracks. The main problem with magnetic disks is that it takes too much time to position the head in the area with the desired data. And if the file is also split into several pieces in different sections, then the time of the reading or writing process increases significantly.

To understand what an SSD disk is, you need to know how it works. To access data for reading or cells for writing, the system only needs to know the address. The controller then simply returns the blocks of data. Time is spent only looking for an address and transferring data - literally milliseconds.
Types of hard drives
By type, SSD can be characterized by form factor and type of interface. There are three main form factors:
- 2,5”. The disc is wrapped in a 2.5-inch case. Provides compatibility between almost all types of systems: laptops, servers, PCs.

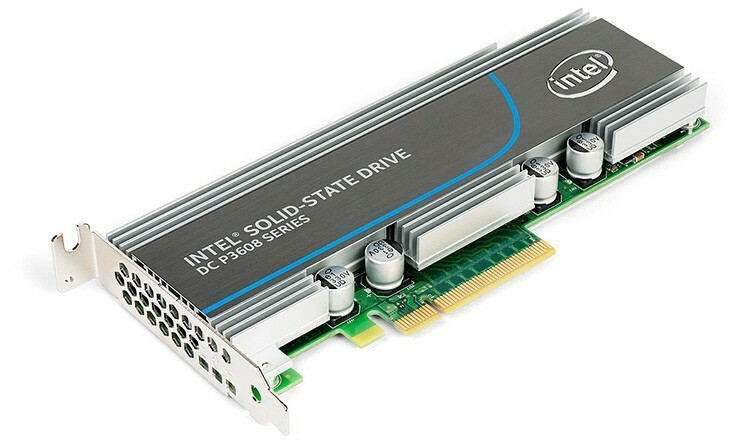
- As a separate board for the PCIe slot. Provides good speed and reliability, uses PCI Express interface.

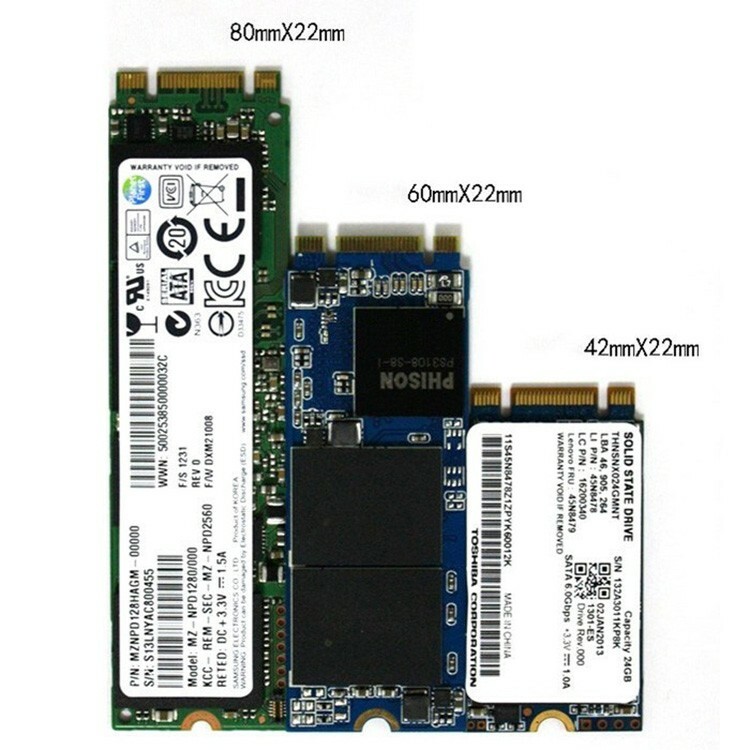
- M.2. A relatively new format, presented mainly in the form of a board that is installed directly on the motherboard in the M.2 connector, which is very compact. This SSD can be found in three different designs depending on the length: 2242, 2260, 2280. The last two digits indicate the length in mm.

There are several other formats that are rare and needed for a narrow range of tasks, such as 1.8 ", 3.5" or mSata.
Interfaces are harder to figure out. This is a mess of standards and specifications. Let's start with the most popular - SATA. To date, there are three main revisions and two additional ones. SATA - Supports up to 1.5 Gbps. Now it is found less and less. SATA II - up to 3Gb / s. SATA III - up to 6 Gb / s. The SATA 3.2 revision received an additional Express prefix. It has speeds up to 8 Gb / s and is backward compatible with other SATA, and, most interestingly, is based on the PCI Express interface. The interface can be implemented in both 2.5-inch and M.2 form factors.
The PCI-E interface is a little easier. It is implemented mainly in M.2 for SSDs. Note that PCI can be multi-lane. The more channels there are, the faster the data transfer rate.
General characteristics of SSD (Solid State Disk)
Let's take a look at the basic characteristics by which you can identify an SSD, analyze what it is, and compare it with an HDD.
Interface and form factor
We have already talked about this a little. Now let's look at this in the context of choice and relevance for different systems. With interfaces, everything is simple - eSATA is now considered the most productive, which in the specifications in some stores and manufacturers can be designated as PCI-E. It is by far the fastest interface.
The form factor must be chosen depending on the type of PC - laptop or stationary. In a stationary, for compactness, you can use M.2, which will take up little space on the board and does not require additional power. Newer laptops also support M.2. For the old, the 2.5-inch form factor is relevant.
Disk capacity and speed
SSD capacities are quite expensive. The most budgetary version of a 32 GB SSD can be bought for about 1,500 rubles, while an HDD for the same money will already have a volume of 160 GB or more. As for the speed, then everything is not so simple. Very often the speed of reading and writing data in the specifications for disks is greatly overestimated. And not necessarily only for little-known small companies, but even for well-known brands. Therefore, one has to focus on reviews and measurements of reputable services and testers.
Type of memory chips
It is interesting that now both types of memory - MLC and SLC - are practically the same in terms of performance and write / rewrite resource. Much depends on the implementation of a particular manufacturer. Before purchasing each specific model, we would recommend looking at the tests and reviews on these gadgets.
Leading manufacturers of SSD drives for PC
Well-known drive manufacturers are in the top. Something special about their implementation does not differ. Moreover, controllers made by Samsung or Intel can be found not only in their own drives, but also in devices of competing brands. The main names in the top:
- Samsung. Produce a wide range of SSDs for a wide variety of tasks;
- Western Digital. One of the oldest media manufacturers. Launches three different drive lines - Green, Blue and Black;
- Intel. Everything is clear here. Reliability and quality;
- Transcend. Known mainly for its flash drives. Now we are releasing full-fledged SSDs.
Which SSD drive is better to buy
If the budget is not limited, then there are no problems. If every ruble counts, then it is better to approach the issue thoroughly. Let's take a look at a couple of models to look out for.
In the category up to 5,000 rubles, you can look towards the Samsung MZ-75E250BW.

The memory type it uses is TLC. The declared read / write speed is 540/520 MB / s. The total storage capacity is 120 GB. A total of 75 TB of data can be stored on disk. On average, users write to their disk from 5 to 30 GB per day, which translates into approximately 10 TB per year. Thus, the resource of this SSD should be enough for about 7.5 years. The SATA interface is used for connection. You can buy a disc for 3600 rubles. And its 2.5-inch form factor will allow you to use it both in a "stationary" and in a laptop.
Samsung MZ 75E250BW
If compactness and space saving are in the first place, then you can consider SSD with M.2. Within 5000 rubles, you can buy Intel SSDPEKKW128G8XT.
This is an M.2 drive with a size of 2280. It should be noted that the free space from the connector to the nearest component must be more than 80 mm. Memory type - TLC. The total disk size is 120 GB. This disk is interesting in that it is connected using the PCI-E interface with 4 channels via the M.2 connector. This means that the tire does not limit the possibilities. SSD and fully allows you to issue excellent write and read speeds - which, by the way, are declared by the manufacturer at 650 MB / s for writing and 1640 MB / s for reading. The total resource is 72 TB of data. The device costs 4290 rubles.
Intel SSDPEKKW128G8XT
In general, prices over RUB 5,000 inherently do not imply big leaps in performance. Only the total disk space changes. By the way, for SSDs, the volume indicator also affects durability. For example, a 120 GB drive with a daily recording of 30 GB will last approximately 7.5 years. With the same recording rate, a 500GB device should last 4 times longer.
The general advice for choosing is this: you need a disk only for the system and programs - you can choose a smaller one, 60 or 120 GB, and store all data, movies, pictures, etc. on another HDD. If you plan to store everything on one SSD, it is better to immediately choose a larger one. PCI-E interfaces are still more expensive than SATA, but they are not limited in speed, therefore, if the budget allows, it is better to choose the PCI-E interface.
Answers to frequently asked questions about SSD
During its existence, SSDs managed to acquire myths and legends, as well as constant questions. We will consider several of them.
Special rules of operation
Many people believe that with proper use of a drive, you can extend its lifespan. This includes various optimizations - disabling caches, indexing, paging file, performing defragmentation. In fact, to a large extent, these actions will not affect the SSD resource. Rather, the decrease in overall performance due to disabling functionality will be less justified than a shared resource increased by a couple of tens of gigabytes.
The only thing that can be advised is to make backups: save your important data on alternative media - the cloud or another disk. Although this advice applies to all media in principle.
How SSD differs from HDD
Read and write speed, shock and vibration resistance, noise level, power consumption and weight. These are the main advantages of SSD over HDD.
What is TRIM in SSD
TRIM is an instruction for ATA interfaces that allows the operating system to tell the disk which blocks of memory can be unused and considered empty. Why do SSD drives need it? It was introduced in connection with the specifics of the operation of solid-state drives. When writing new data to a cell, the SSD cannot simply take and replace the old data with the new one. He has to first read the data into the cache, clear the cell, and then write it down - while the access speed decreases significantly. TRIM has solved this problem. The system and the drive are constantly exchanging information about which cells are no longer needed, and upon a TRIM signal, it resets these cells to zero. The next time the SSD is written, it just immediately quietly writes data to it.
Do i need an SSD for gaming?
Here, too, not everything is so simple. Firstly, you can't expect a significant increase in FPS in games from using an SSD. The solid-state drive will be relevant when loading worlds and levels - locations will load faster. There is a possibility that the SSD drive can help in cases where performance is limited by the amount of RAM, when this data is thrown into the paging file. But in such a situation, changing HDD to SSD instead of increasing the "RAM" is a dubious pleasure.
By the way, there is an interesting video of testing popular games on different discs:
If you have experience with SSD, then you can share it with other users in the comments.



