Today, when repairing the water supply and heating systems, instead of metal pipes, they are installed with polypropylene analogs. This is due to the durability, lightness and easy maintenance of the material, as well as the ability to carry out installation on its own quickly and reliably.

Specificity of brazing polypropylene pipes
The principle of soldering polypropylene pipes is based on the thermoplasticity of the material. The polymer, under the influence of temperatures above + 200 ℃, quickly softens, it also takes a few seconds to harden under normal conditions. During the contact of the molten edges of the blanks, a polyfusion process occurs, the result of which is a monolithic connection of the elements. Thermal action on the end parts of the pipes does not lead to changes in the quality characteristics of the material.
Another option involves the use of special fluids that cause a similar process due to the chemical reaction of polypropylene with active components (organic solvents). In other words, this approach is called “cold welding”. This technology of soldering polypropylene pipes with your own hands is easy to implement, but it has limitations in application, which is reflected in its relatively low popularity compared to polyfusion.

Methods for joining polypropylene pipes
The assembly of the pipeline from polypropylene blanks is carried out in two ways: direct and by means of additional connecting elements for various purposes. The first option is relevant for elements whose diameter exceeds 40-63 mm, since the products have rather thick walls. It is important to observe several conditions here:
- identical dimensions in cross section, thickness;
- exact coincidence of the end edges;
- strict alignment.
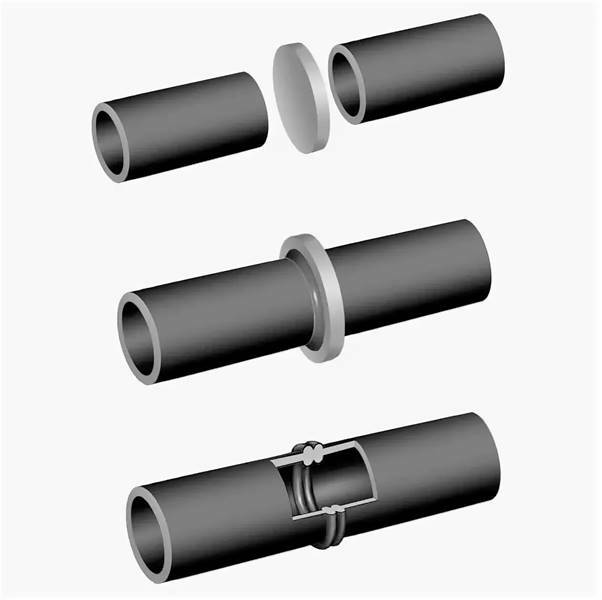

The method of socket welding is used for thin-walled (up to 4.5-5 mm) products with an outer diameter of 16 to 40-63 mm. Such blanks are relevant for the installation of a water supply and heating system in the residential sector. Here, for the assembly of highways, additional connecting fittings are used, one or all of the branch pipes of which are made of thermoplastic polymer. It is worth noting that the inner and outer diameters of the parts used should be close in values, but differ upwards in favor of the second size.

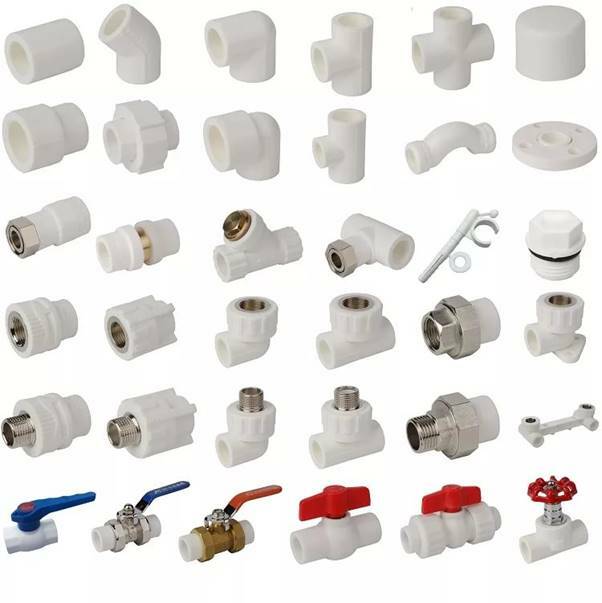
Couplings are classified into several main groups for their intended purpose:
- adapters by size;
- connectors at different angles;
- splitters from one to several channels;
- elements with a threaded tip for the formation of collapsible assemblies;
- taps, valves.

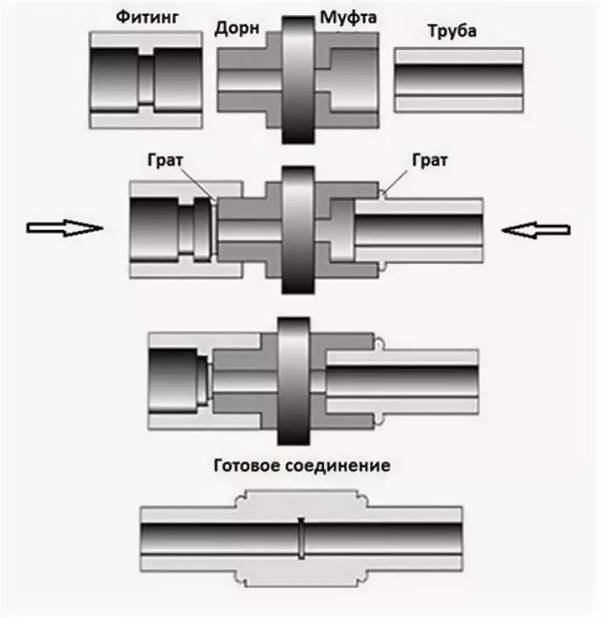
For the soldering of polypropylene pipes in hard-to-reach places and in general using the coupling technology, compact equipment is used, available for the home craftsman. Here the essence of welding is that the workpieces are inserted into an additional connector. Compared to the direct (docking) method, it is easier to implement, therefore, it is often performed without the involvement of professional help.
What is required for installation work
Working with polypropylene pipes consists in cutting blanks, preparing end edges for installation, heat treatment of elements and forming a joint. The implementation of the project requires a small arsenal of soldering tools:
- measuring instruments, bench square and marking materials (pencil, marker);
- roller pipe cutter or special scissors;
- rags with degreaser;
- apparatus for soldering certain polypropylene pipes;
- thick gloves with anti-slip coating.
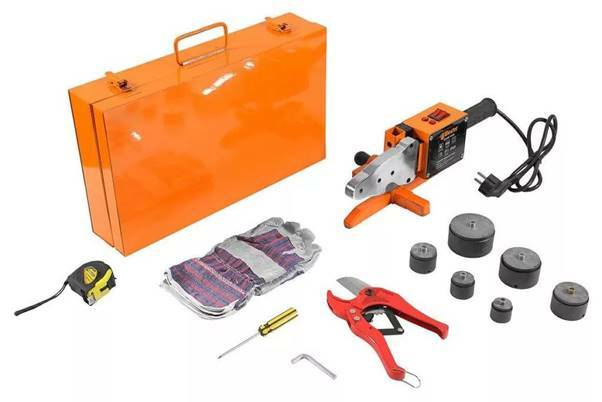

The cutting tool must be comfortable and serviceable. The blade is checked for defects, sharpening. If possible, shortcomings are corrected, if not, new scissors are purchased. It is also important to keep track of the squareness of the cut, which must be clean and even. Such requirements exclude the use of a hacksaw blade (saw, jigsaw) or a grinder.

To ensure a tight and reliable connection between polypropylene blanks, it is necessary to prepare the working edges. The process includes removing dust, dirt, burrs, moisture, and degreasing surfaces. To do this, you can use a ready-made general construction compound or alcohol (ethyl, isopropyl).
For large-scale projects with large-diameter pipes, mechanical, electro-hydraulic equipment is used. The composition of such devices includes a bed, a control unit, grippers with a seal, a facer, a disc heating element, a dynamometer. Fixation, displacement and adjustment of the position of polymer blanks is carried out by movable centralizers. They are manually operated by means of a lever. Another option is a hydraulic drive.
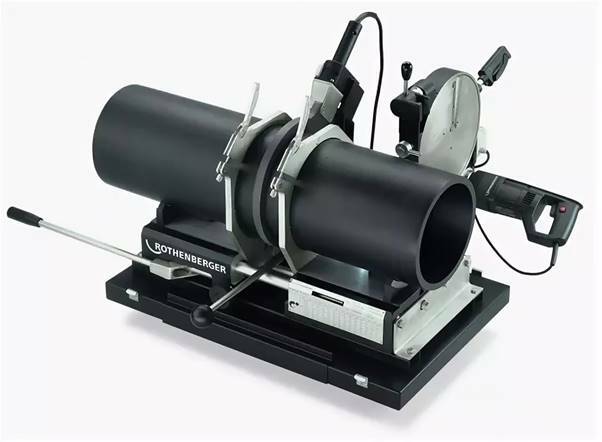

The welding machine for working with pipes of small diameter and thickness is structurally represented by a stand, a handle, an adjustment unit, a heating element in the form of a narrowed plate (xiphoid) or a pin (cylindrical). Special attachments (sleeve-mandrel) of various diameters are attached to the latter. As a rule, it is permissible to simultaneously install several removable gear (under holes or in the form of clamps) in order to carry out continuous installation of lines from different-sized channels. A hex wrench is included for fastening parts.

How is polypropylene pipes soldered
The instructions for soldering any polypropylene pipes by means of thermal effect on products assumes compliance with standardized or manufacturer-recommended time intervals. They cover heating and the formation of a nodal connection between the elements of the line. The process itself is carried out in different ways depending on the equipment used and the size of the pipeline elements.
General technological methods of welding polypropylene pipes
How to properly solder large diameter polypropylene pipes? The butt welding process involves two steps. The workpieces are pre-installed and fixed on the equipment in a predetermined position. The edges of both parts at once are processed with a facing tool (special rotating disc). Then it is replaced with a flat heating element. After its elimination, after a certain technology time, the workpieces with molten edges are pressed against each other to carry out the polyfusion process.
Socket welding technology requires attention with respect to the time for melting the walls and compressing the elements.
Below is a table of soldering temperatures for thin-walled polypropylene pipes, which is worth relying especially for a novice craftsman.
Characteristic value | Outside diameter (mm) | ||||||
| 16 | 20 | 25 | 32 | 40 | 50 | 63 | |
| Heat treatment area (mm) | 13 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 23 | 26 |
| Melting Timer (sec) | 5 | 7 | 8 | 12 | 18 | 24 | |
| Node adjustment timer (sec) | 4 | 6 | 8 | ||||
| Connection Hold Timer (sec) | 6 | 10 | 20 | 30 | |||
| Polymerization timer (sec) | 120 | 240 | 360 |
The joint is formed by means of the inner wall of the fitting and the outer wall of the pipe. Areas are subjected to thermal effects by means of special nozzles for soldering equipment, heated to a temperature of + 260 ℃. Next, the blanks are inserted into each other and held in place for the minimum required time.
Features of working with pipes with aluminum reinforcement
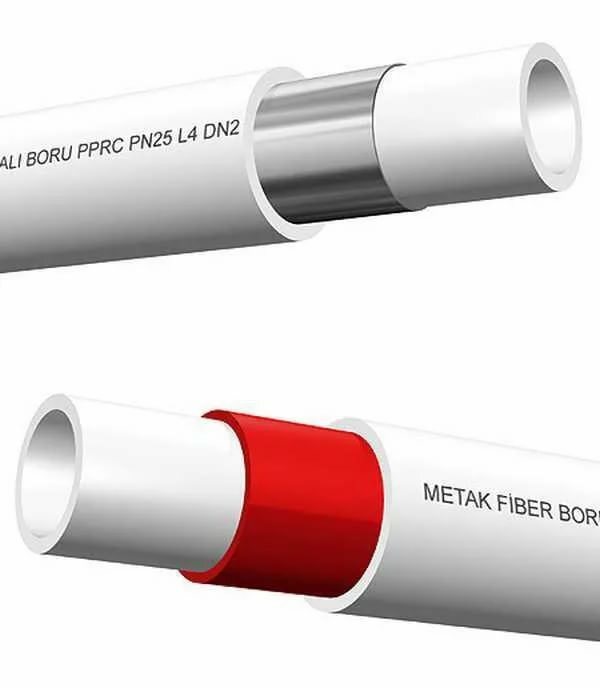

Polypropylene has the property of warm expansion, which limits the use of the material in conditions with high temperatures, changes in its indicators. The disadvantage was corrected by reinforcing the pipes with aluminum or fiberglass. In the case of the first, difficulties do not arise during soldering and operation of the lines.
Metal reinforcement can be installed on the inside of the product or under the outer shell. The outer layer with aluminum foil must be removed before brazing. There are three reasons for this:
- additional heating is required;
- metal-plastic blanks have a larger outer diameter than without reinforcement or with fiberglass;
- aluminum and polymer form a weak bond during welding.
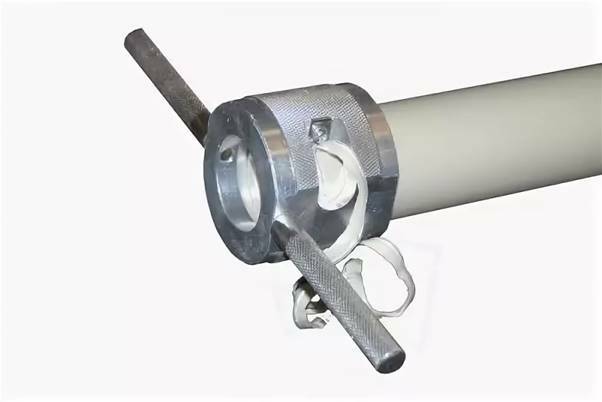
To carry out the work, a shaver is used - a duralumin hollow cylinder with steel blades located inside. Additionally, for ease of use, a removable rod-shaped handle can be inserted. Here, a limitation on the thickness of the cut and the depth of the processed area is provided in advance, so there is no need to monitor the parameters.

Internal stripping is carried out to exclude direct contact of aluminum with the transported liquid. This can lead to activation of electrochemical processes, destruction of the reinforcing foil, pipe delamination, depressurization of the contact assembly. Here, facers are used to prepare workpieces for welding. This device is similar in structure to the shaver, only the blades are located on the inner end.

Specificity of work in conditions of negative temperatures
Installation work at low temperatures involves making changes to the key time intervals for heating and fixing the workpieces. But the installation features are not limited to this. The impact of frost on the polymer is reflected in the hardness of the material - it becomes brittle, which complicates cutting, requires more attention during transportation.
The fragility issue is solved only by the accuracy of the work. It is best to cut in a heated room. The limit values of permissible temperatures are in the range of 0- + 5 ℃. Lower rates lead to crystallization processes that are not bypassed by polymeric materials. In such conditions, there is a high risk that the pipes will begin to crumble.

Thermal exposure guidelines are based on room conditions. The lower the thermometer reading, the longer it takes to heat the polypropylene. Based on the practice, the masters recommend that you first bring the material to + 20 ℃, then use a standardized timer. At the same time, it is impossible to heat the device over + 260 ℃, as this can negatively affect the quality of the pipes.
There is an opinion that all standards when working in the cold should be increased up to 50%. This does not apply at all to commit times. The connection of the elements here must be carried out in an accelerated mode, so that a full-fledged polymerization process is possible with rapid cooling. Delay in this case will lead to the fact that the node will be of low quality, will not last long due to early depressurization.
Impact of errors on welding quality
Experts note that the most common mistakes are the neglect of the requirements for the preparation of pipes and according to time standards. Degreasing is often skipped, inattentive to the condition of the edges, cleanliness and dryness. Such errors lead to a violation of the solidity of the connection.

Overheating of the walls of polypropylene pipes leads to a narrowing of the inner diameter of the nodal joint. It also occurs with excessive compression. As a rule, it is impossible to clean the duct. And such a malfunction, along with distortions, is the cause of a rupture or clogging of the channel.
In rare cases, early failure of the assembled line is justified by dissimilar materials relative to the manufacturer. This happens even after professional editing. The reason is that each manufacturer works according to its own technology, uses its own recipe. As a result, pipes may have different heating, fixing and cooling rates. Therefore, it is worth using blanks with fittings from the same manufacturer.



