It is difficult to keep up with modern technologies, as well as fashion, but those who constantly monitor their development never fail. This is especially true for the construction industry. Now there are many building materials, which are distinguished by moisture resistance, low weight, good heat, soundproof characteristics and fire safety. All this can be attributed to foam glass, which will be discussed in today's review by the editors of the online magazine HouseChief. Our experts will tell you what kind of material it is, what properties it has, where it is used.
Read in the article
- 1 What is foam glass, the history of its creation
- 2 Specifications
- 3 Advantages and disadvantages of the material
- 4 Varieties of foam glass
- 5 Areas of use
- 6 Features of installation of foam glass
- 7 A few words in conclusion
What is foam glass, the history of its creation
Foam glass is a heat-insulating material that is obtained through heat treatment at a temperature of about 1000ºC of silicate glass and gas-generating raw materials (anthracite, coke, soot, etc.). As a result, foaming occurs, leading to an increase in the volume of the mixed components by about 15 times.

The resulting mass is molded and cooled without forced cooling, which makes the material strong and durable.
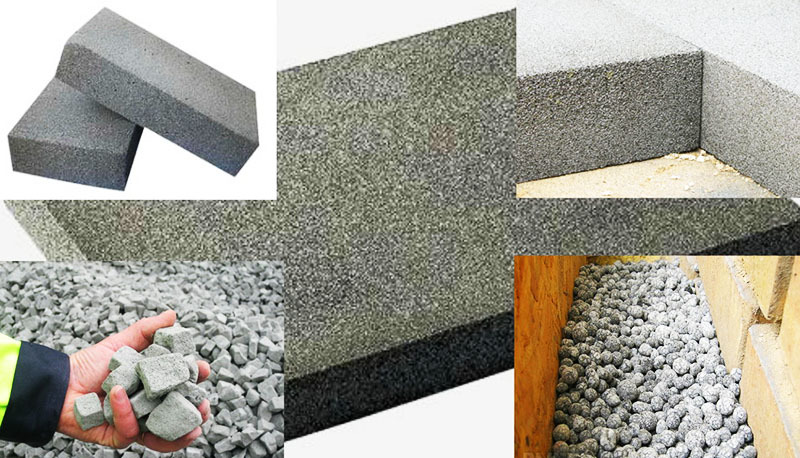


Despite the fact that foam glass was invented in the 30s of the last century by the Soviet physicist-crystallographer Academician Alexander Isaakovich Kitaygorodsky, for the first time it was applied in practice in Canada. Only half a century later, after improving technology and reducing production costs, the material gained recognition and began to be used as an inexpensive and effective insulation.
Specifications
The density of the foam glass is quite low and amounts to 100-250 kg / m³. For comparison, for natural dry wood this figure is 550-750 kg / m³. That is why it was originally supposed to be used as a floating building material.
Its weight is 70-170 kg / m³, and the sound insulation level of a 100 mm thick block is 52 dB.
Foam glass has a fairly high compressive strength - 40-100 t / m².
The thermal conductivity of the material at average room temperature is 0.04 W / mK. For comparison, for dry coniferous wood, this indicator is 0.09 W / mK. In terms of sound absorption, porous glass is practically on a par with mineral wool - 45-56 dB.
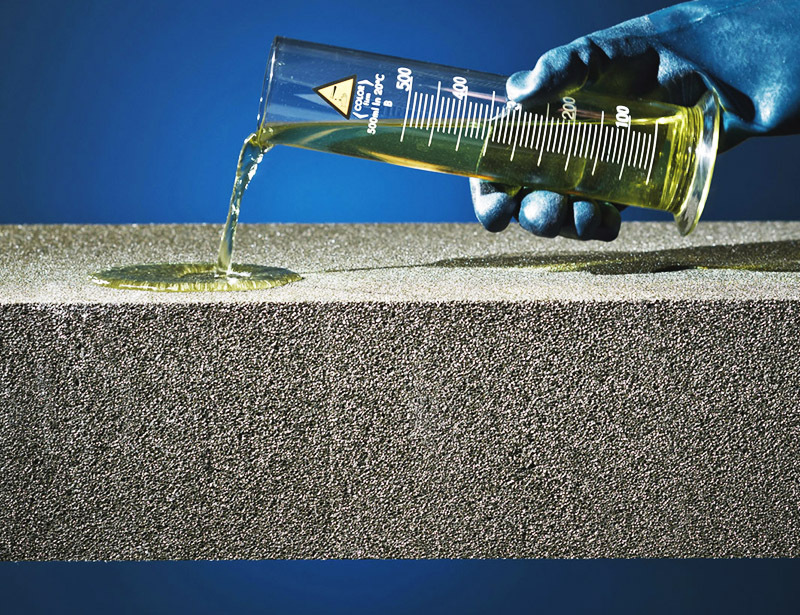
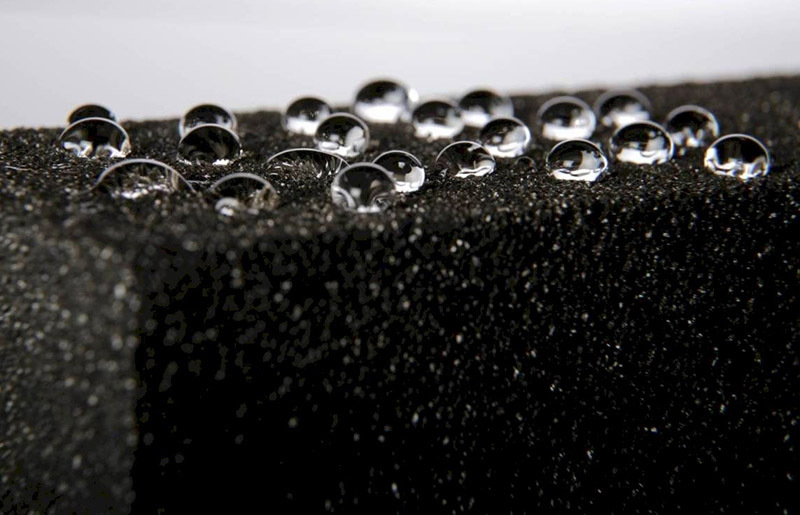
The water absorption coefficient of foam glass is no more than 2% of the volume. That is, the material practically does not absorb moisture, and this is with practically zero vapor permeability - 0.005 mg / (m · h · Pa). These characteristics make foam glass an ideal vapor barrier.
Cellular glass is resistant to extreme temperatures. The material retains its properties even at + 300ºC, and special additives increase its heat resistance up to + 1000ºC. Also, foam glass perfectly tolerates cold and can even withstand exposure to liquid nitrogen (-200ºC).

Advantages and disadvantages of the material
Foam glass as a heat-insulating material has both its supporters and opponents. Some are attracted by its merits, others point to its disadvantages. So, let's see what is the appeal of this material. Its advantages include:
- high heat and noise insulation characteristics due to the structure of the material;
- versatility thanks to which foam glass can be used for wall insulation, floors, roofs, foundation and facades;
- high resistance to temperature extremes in a wide range;
- long service life, reaching 100 years;
- environmental friendliness;
- resistance to erosion and oxidation;
- fire safety. The material does not burn, and at temperatures above 300ºC it simply melts without the release of smoke and toxic substances;
- not susceptible to fungi and mold;
- chemical inertness;
- hygroscopicity and vapor permeability;
- preservation of shape throughout the entire period of operation;
- ease of installation. Foam glass granules are simply poured into the prepared space, and blocks, if necessary, can be cut with an ordinary hacksaw.

As you can see, cellular glass has a lot of advantages. So why the opponents of this material do not like it. Among the disadvantages, they note:
- High cost due to the complexity of production.
- Low level of steam conductivity due to which it is required to create an additional vapor barrier.
- The need to strictly adhere to the installation technology.
- Shock susceptibility.

Varieties of foam glass
The modern construction market offers foam glass in two forms: granules and slab blocks. Granulated cellular glass - microporous balls with a diameter of 1.5-20 mm. This form is most often used for insulating floors, ceilings and walls. The granules are added to the adhesive and kneaded. As a result, a mixture with high thermal insulation characteristics is obtained.
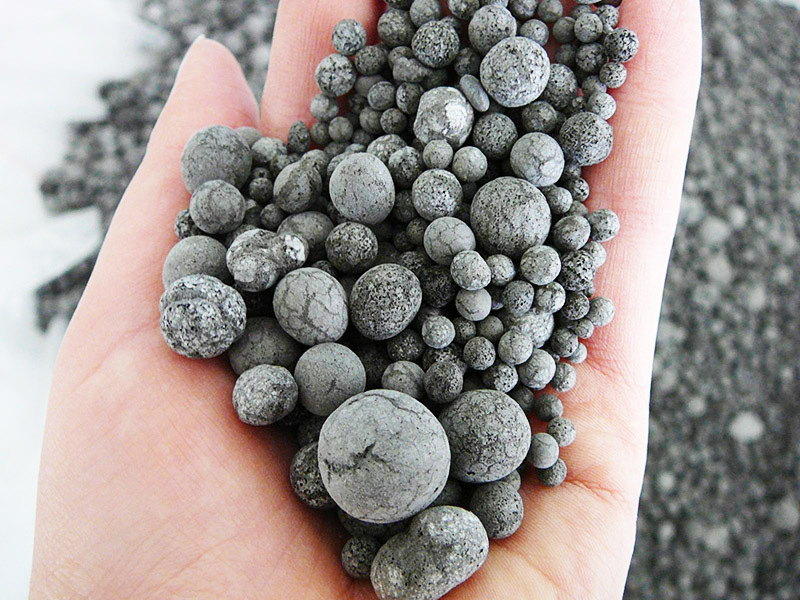

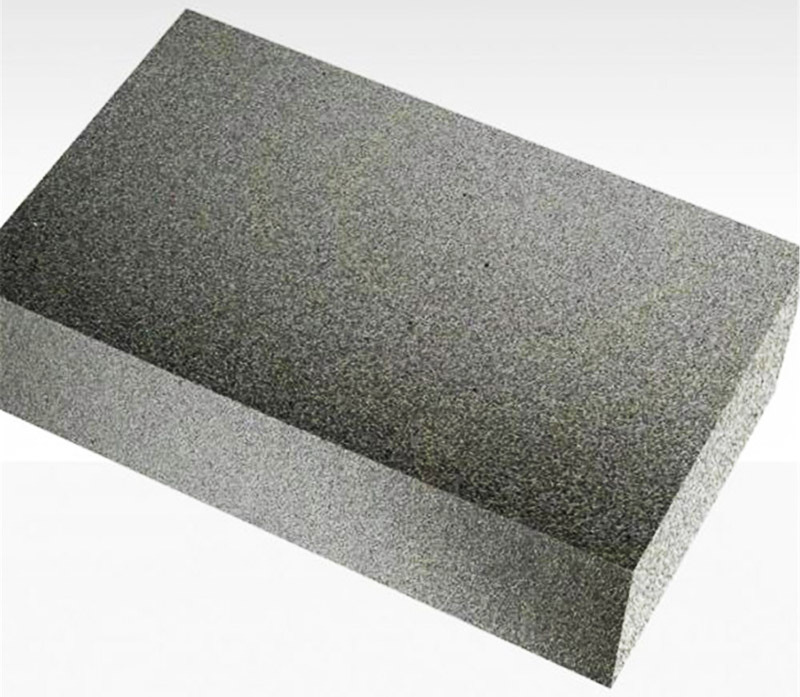
Block foam glass has the form of slabs with dimensions of 450 × 600 × 60-120 mm. Cellular glass blocks are used to insulate the foundation, basement, facade, ceilings and floors. Plates are resistant to deformation, do not change dimensions and withstand significant operational loads. If necessary, the block glass can be easily cut with an ordinary hacksaw.


A comment
Mikhail Starostin
Head of the team of the repair and construction company "Dom Premium"
"The technical characteristics of both forms of foam glass are similar and when choosing, you need to be guided by the ease of installation of insulation."
Areas of use
Due to its high technical characteristics, foam glass, despite the high cost of the material, has received a wide range of applications in construction. Its main purpose is noise and heat insulation. Foam glass can be used as insulation in mass construction and the agricultural industry, as well as in the implementation of individual projects. An important component of the use of this material is environmental safety.
The modern construction market offers a large selection of thermal insulation materials, but in some areas the use of foam glass is more efficient and expedient:
- erection of high-rise structures. Due to its high strength and fire resistance;
- thermal insulation of large areas;
- construction of structures, the operation of which is associated with high humidity (baths, saunas, swimming pools, SPA-salons and water parks);
- restoration of old buildings;
- thermal insulation of various types of underground structures;
- environmentally friendly thermal insulation material for the construction of buildings for the medical, pharmaceutical and food industries;
- due to the ability to withstand temperature extremes in a wide range, it is used for thermal insulation of pipelines;
- in the chemical and oil industry, especially in the northern regions;
- due to its high fire-fighting characteristics, it is used in the nuclear industry.

Each type of cellular glass is used exactly where it is needed most. For example, panels are used for external insulation of facades, thermal insulation of foundations and pipelines, as well as thermal protection of furnaces.
Granular foam glass is used to insulate floors, ceilings, and wall cavities in houses. Due to the frost resistance of the material, it is used in some European countries for the arrangement of the roadway.

Features of installation of foam glass
Foam glass, like other building materials, has some features that must be taken into account when working with it. Let's consider the most basic ones.
When insulating walls, cellular glass can be used both outside the building and inside. Remove old finishes and dirt before installing the units. A layer of cement or special adhesive is applied to the prepared surface, on which a foam glass plate is applied and pressed tightly. From above, the material is finished plaster. In this case, the arrangement of additional steam and waterproofing is not required.
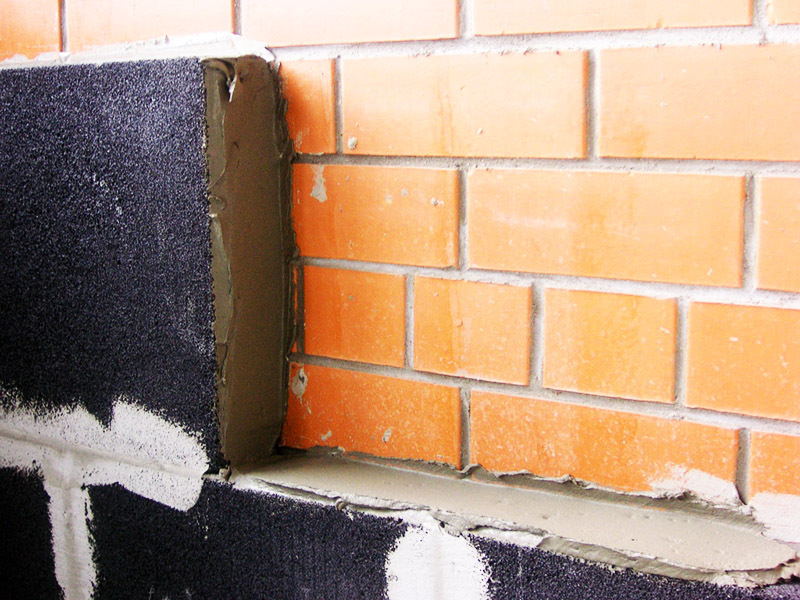

Thermal insulation of floors can be performed using foam glass blocks, chips or granules, but it is better to use panel material. First of all, a sand base with a thickness of 50 mm is poured, on which foam glass plates are laid. The joints can be sealed with polyurethane foam, and a reinforced screed can be arranged on top of the thermal insulation. After that, you can finish the floor.
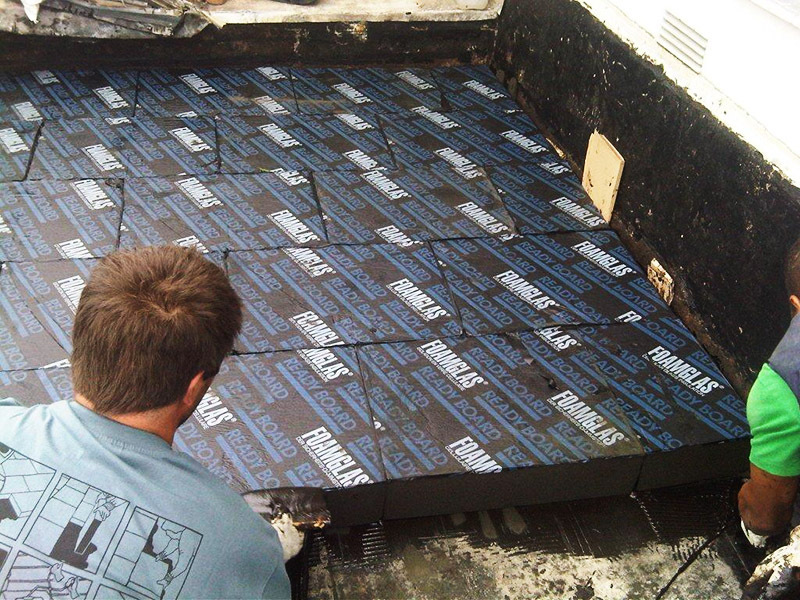

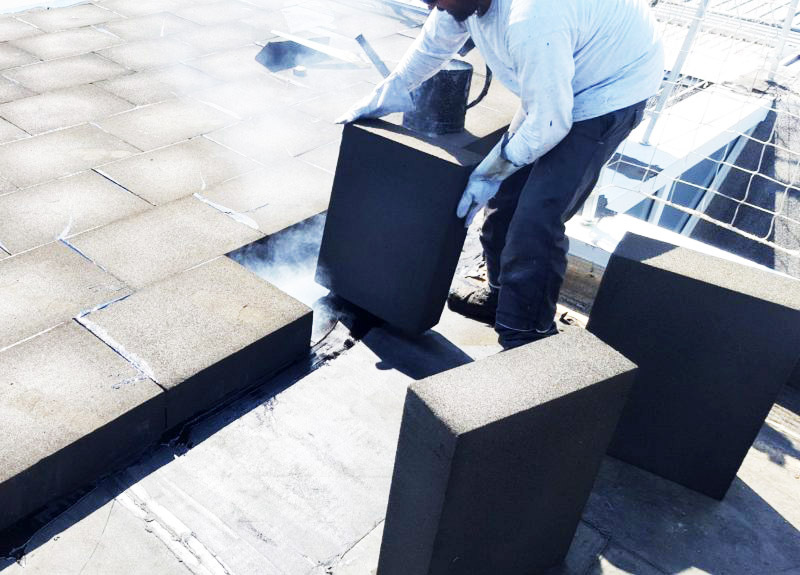
The roofs of buildings are most susceptible to the destructive effects of moisture, wind and cold. The use of foam glass for thermal insulation will be the most optimal solution. If the attic space is not residential, then it will be enough to insulate the floor around the perimeter in the same way as in the above case.

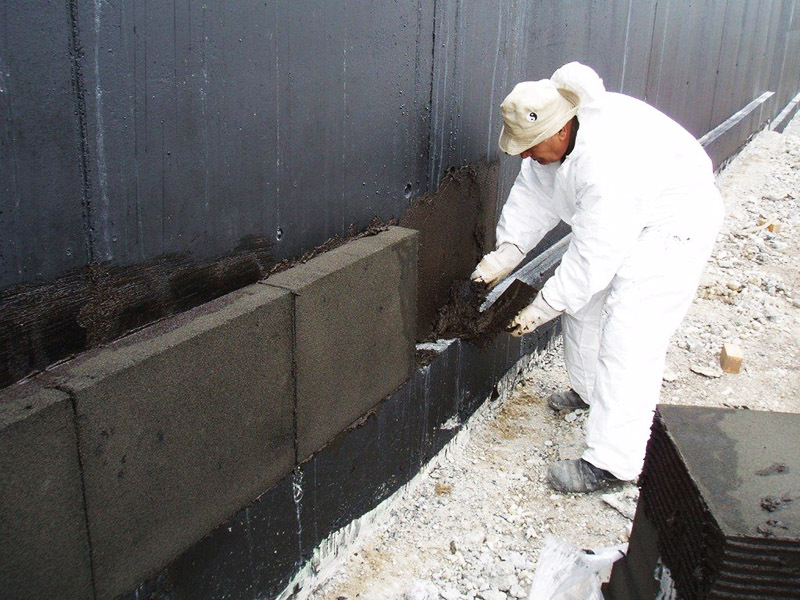
Insulation of the foundation is a very important point in the construction of various structures, especially if the building is located in a lowland or in a swampy area. In this case, the base of the house often becomes damp, and walls, floors and ceilings become wet from it. As a result, the formation of mold, mildew, rot and, ultimately, the destruction of structures occurs. Constant repairs will not save the situation, therefore, it is recommended to insulate it at the stage of building the foundation as with outside and inside with foam glass plates or granules mixed with a special adhesive solution.

Most private houses and summer cottages are equipped with saunas, in which, due to high humidity and temperature changes, an aggressive environment is formed. It is recommended to use foam glass plates for insulation and vapor barrier. The very procedure for carrying out thermal insulation does not differ from that which is carried out in ordinary rooms.
A few words in conclusion
Cellular glass is a modern, high quality and very light material used for heat and sound insulation. It is still used in luxury construction, but foam glass will become more affordable in the near future.
Was our article helpful to you? Would you use foam glass to insulate your home if the price was reasonable? Share your opinion and rating with us and other readers. Maybe you already have experience with this material, and you can tell us something new?