In order for a wooden flooring to last long enough, it is necessary to competently approach its preparation and arrangement. The correct calculation of the distance between the floor joists will allow you to form a reliable structure. Attention is paid to both the structural elements themselves and the distance between them. If desired, everyone can understand the calculation procedure and perform it on their own.
Read in the article
- 1 Lag functions and requirements for them
- 1.1 Base for subfloor and logs on poles
- 1.2 Interfloor lags
- 2 Materials for lathing
- 3 The main reasons why calculating the distance between lags is so necessary
- 4 What you need to consider when calculating: initial data
- 5 The correct calculation of the distance between the floor lags with your own hands
- 5.1 Length calculation
- 5.2 Section calculation
- 5.3 Step lag depending on the floor covering
- 6 Examples of calculating the lag for a wooden floor
- 6.1 Standard panel house
- 6.2 Frame building
- 7 Errors made when calculating the lag for plywood, and their consequences
- 8 How else can you calculate the size and number of elements for installing the floor along the logs
- 8.1 Online calculators and computer programs
- 8.2 Average tables
- 8.3 Professional design organizations
Lag functions and requirements for them
Lags are used as a base for flooring in various situations. Such structural elements are in demand when constructing a subfloor, on pillars and interfloor ceilings. Each option deserves special attention.
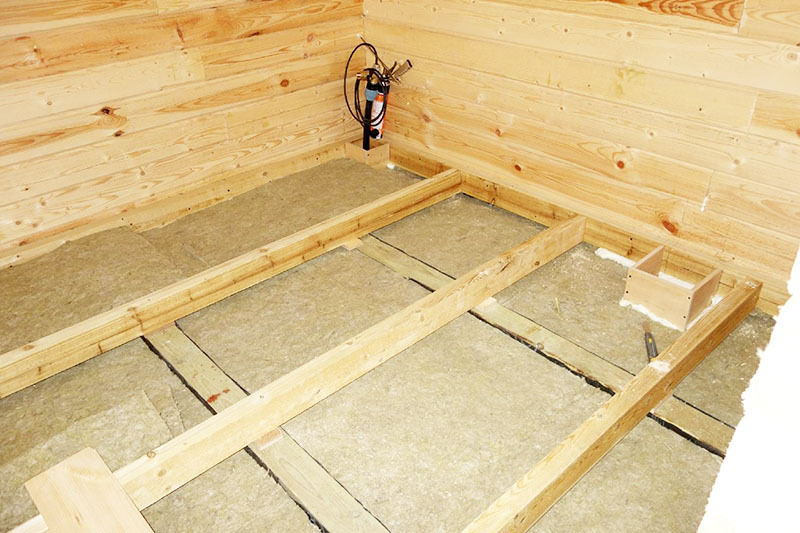

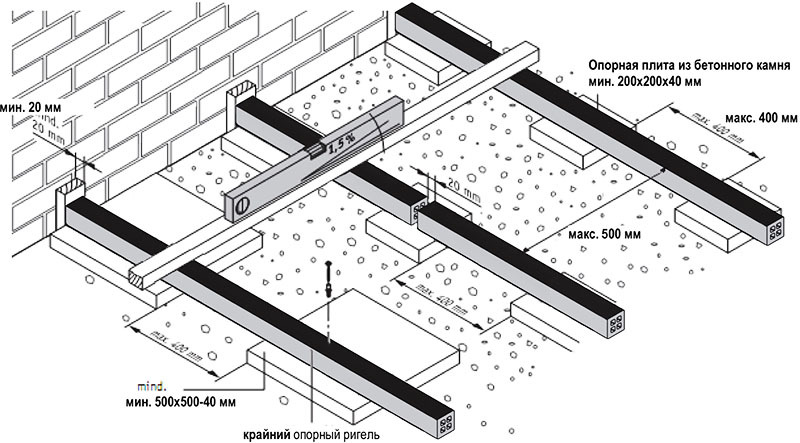
Base for subfloor and logs on poles
The joists used as a base for the subfloor are mounted on the existing floor. They are made on a concrete base, an earthen floor, on a different surface. The main function of these structural elements in this case is to increase the duration of operation of the rough and finished floor, to prevent its deformation and destruction.
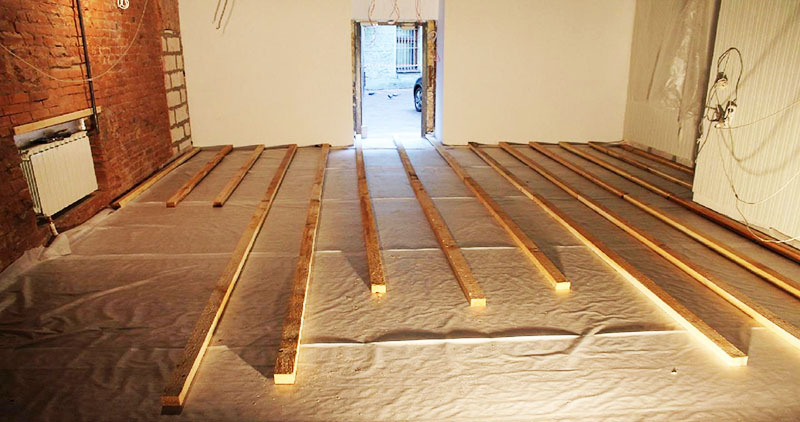

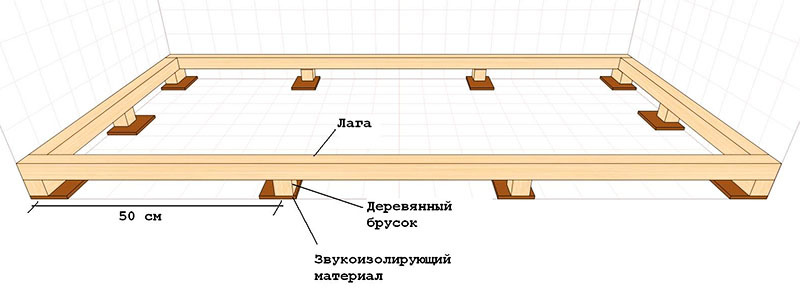
In some cases, the logs are mounted on support pillars located in the subfloor of the house. Their main function is to transfer the load to building foundation. They take on the load taken by the floor covering during the operation of the building, and then transfer it to the support pillars.
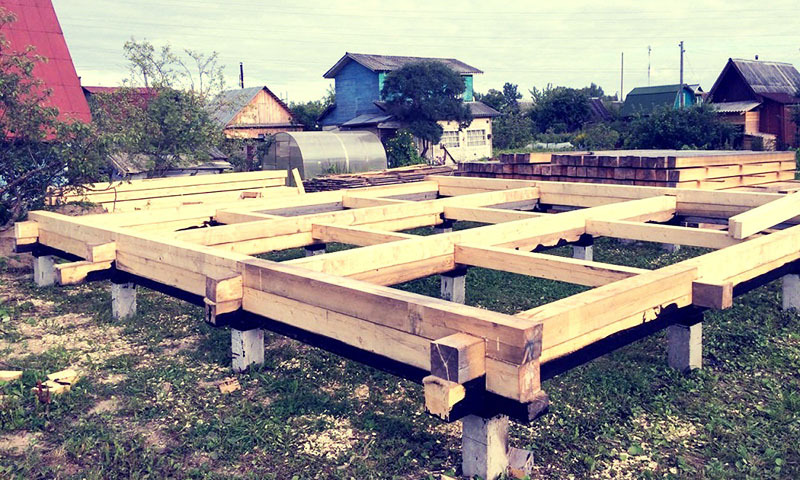

Interfloor lags
In the construction of some buildings, logs act as interfloor elements. They perceive static and dynamic operational load, and then redistribute it between other floor elements.
Increased requirements are imposed on such structural elements. Noteworthy is the cross-sectional area and the distance between the supporting elements.
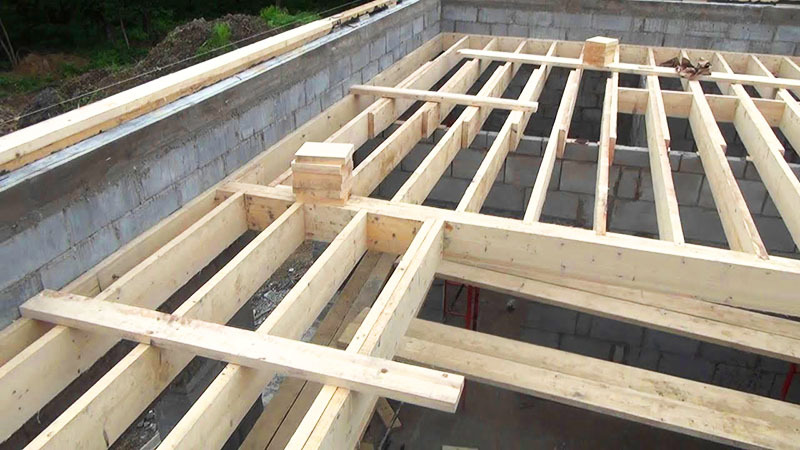

Materials for lathing
For the construction of the lathing, various materials can be used that have a sufficient level of strength in the presence of a load, a low coefficient of deformation and always even.
The choice is most often made in favor of:
- wood;
- metal;
- reinforced concrete;
- plastic;
- a compound based on synthetic resins.

A comment
Mikhail Starostin
Head of the team of the repair and construction company "Dom Premium"
"The most widespread are logs made of wood, for the manufacture of which wooden beams are used."
For the construction of the lathing, mainly coniferous wood is used. Beams made of pine, spruce, and fir are cheaper than elements made of larch. But the latter has a higher strength and resistance to decay processes.
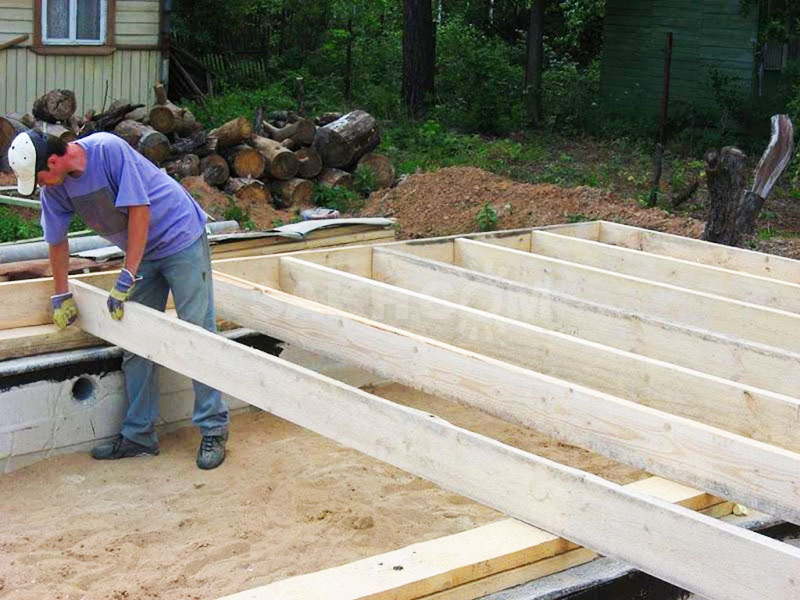

The main reasons why calculating the distance between lags is so necessary
The need to calculate the distance between the lags is dictated by ensuring a sufficient level of strength and durability of the structure being formed. A correctly performed calculation will avoid the characteristic squeak and sagging of the floorboards when walking. In addition, the number of logs to be laid and, consequently, the cost of construction work directly depends on the selected distance. With a minimum distance, strength will increase significantly, and with it, costs. At the maximum, difficulties may arise directly in the process of operation.
Attention! The main reason for the need to calculate the distance between the lags can be called the search for the optimal value that allows you to form a high-quality and reliable floor covering at minimal cost.
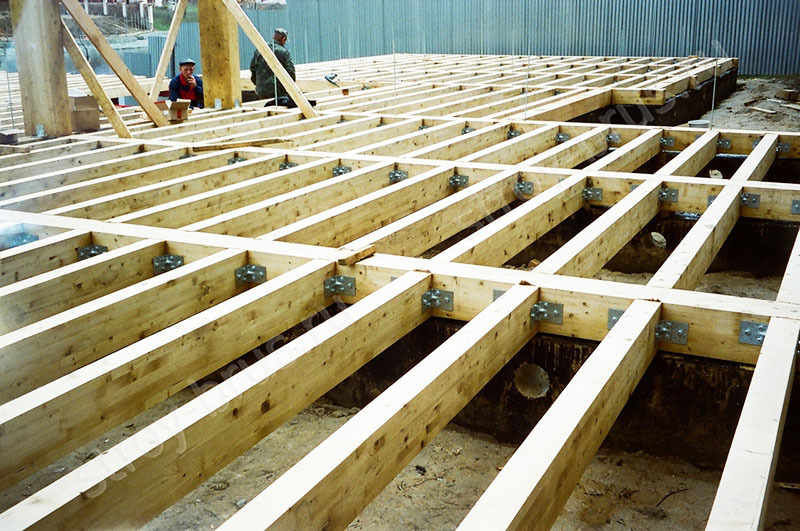

What you need to consider when calculating: initial data
To correctly calculate the required amount of lag, the following values are required:
- The thickness of the floorboards or slabs to be installed in the future.
- Maximum service load per square of floor surface.
- The distance between the walls or the number of anchor points.
Attention! This data is sufficient to calculate the maximum pitch between the lags and the dimensions of the cross-section of each element.
The correct calculation of the distance between the floor lags with your own hands
The calculation of the laid elements involves the sequential determination of their length, transverse dimensions and pitch. By following the guidelines below, you can easily find all relevant parameters.
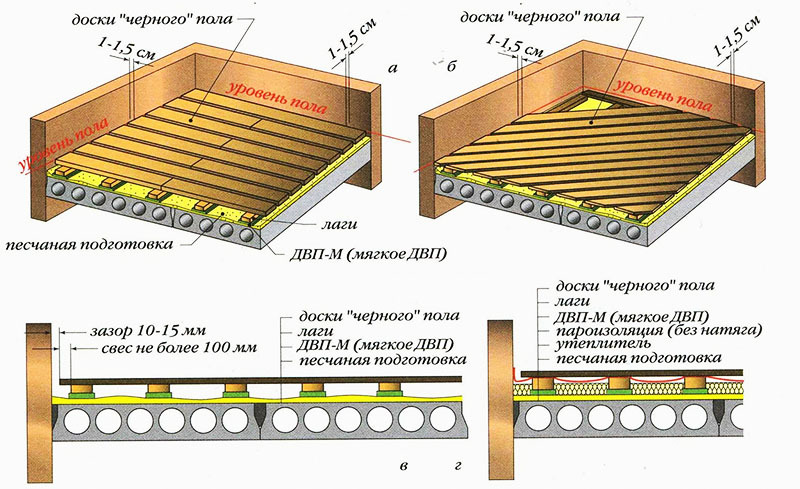
Length calculation
To determine this parameter, you need to know exactly in which direction the laying is done. The length of the lag in this case will be numerically equal to the length or width of the room minus 2-3 cm. In this case, it will be possible to avoid deformations that the assembled structure may undergo when the air temperature changes.
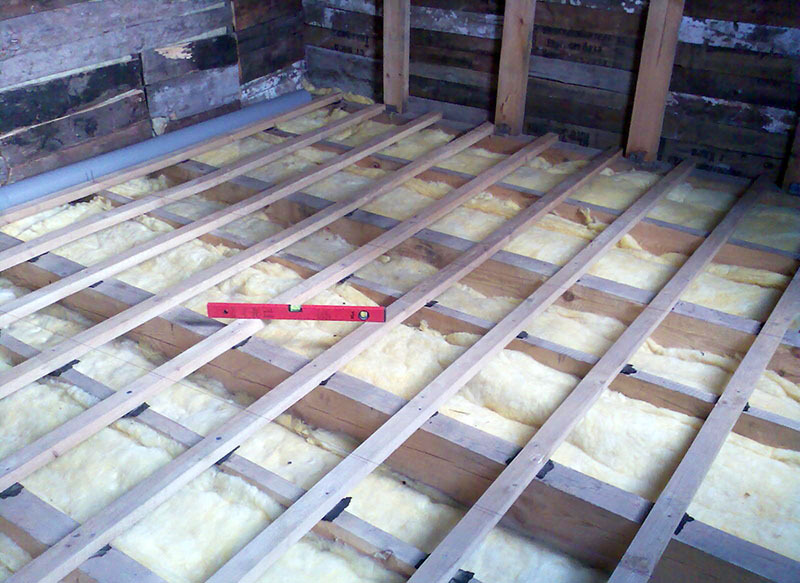

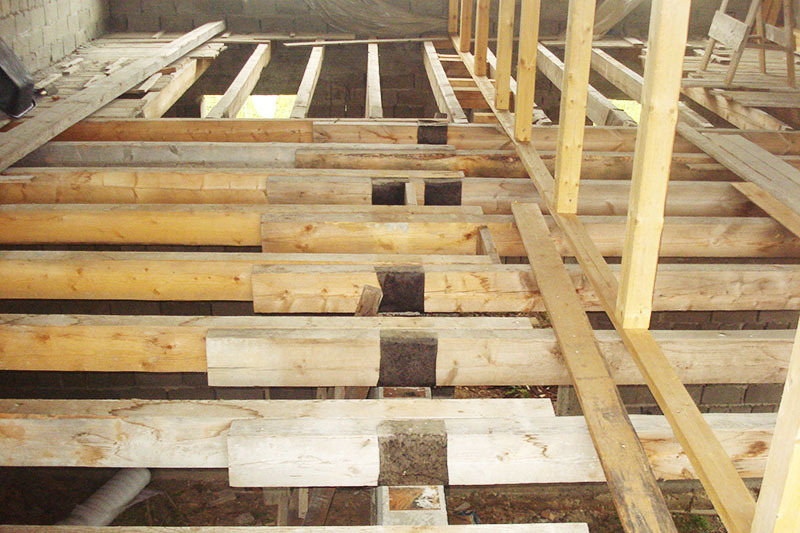
For the manufacture of floor logs, it is preferable to use solid lumber. However, this is not always possible. In this case, they resort to splicing two elements. They do it in half a tree. To ensure sufficient rigidity and strength, galvanized linings are used.
In this case, the following rules are adhered to:
- For the location of the splice point, some kind of support is chosen. A pivot column is desirable.
- Splice points on adjacent lags should be staggered.

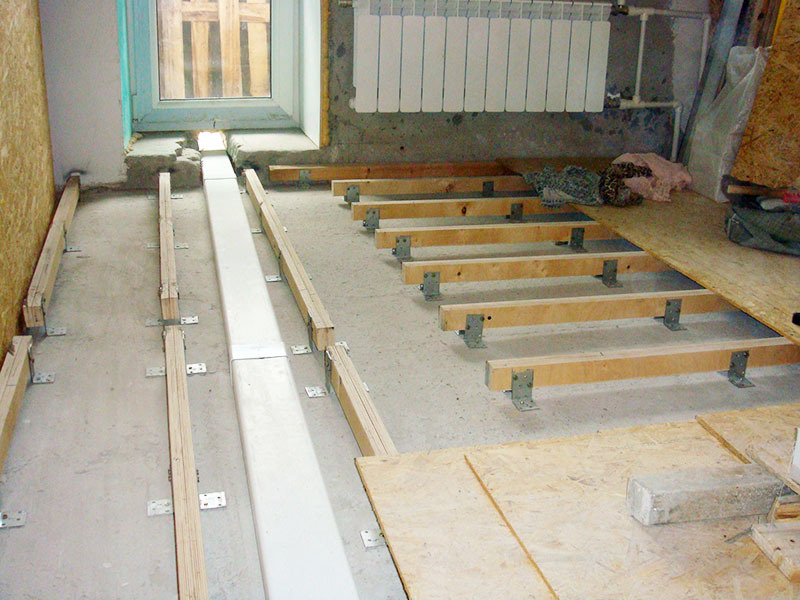
Section calculation
There are usually no problems with determining the length of one element, but calculating the cross-section can cause serious difficulties. When choosing a thickness, be sure to take into account the material of the element and the characteristics of the floor to be installed. When calculating the dimensions of the cross-section, the maximum load and the distance of the anchor points are taken into account.

A comment
Mikhail Starostin
Head of the team of the repair and construction company "Dom Premium"
"For living rooms, the maximum load is 300 kg / m2."

With two-meter spans, bars with a cross-sectional size of at least 110 × 60 mm are chosen, with three-meter spans - 150 × 80 mm, with four-meter spans - 180 × 100 mm. The longer the span, the larger the cross-sectional dimension of the timber to be laid should be.
The section of the timber to be laid, as a rule, has a rectangular shape. To ensure sufficient strength and rigidity, it is laid on the edge. Thanks to this technique, it is also possible to minimize the amount of material used.

If the lag is calculated for a technical room, the requirements here may differ. In this case, the lifting capacity of the supports must exceed 300 kg / m2. The real load is determined by calculation, based on what equipment will be installed, how much area it will occupy.
If metal or reinforced concrete is used for the manufacture of supports, the cross-sectional dimensions of the lag can be much smaller. Such elements are better resistant to external influences than wood.

Step lag depending on the floor covering
When determining the step between the lags, the parameters of the boards that are planned to be used for the flooring device are taken into account. The thicker the boards to be laid, the larger the step between the logs. So, if the thickness of the boards to be laid is 2 cm, the step can be 30 cm. An increase in transverse dimensions up to 2.5 cm allows the elements to be positioned at a distance of up to 40 cm, with 3 cm - up to 0.5 m. calculations, you can use the average formula: each additional 0.5 cm of transverse dimensions allows you to increase the step by 10 cm.
Sometimes OSB or plywood acts as a flooring. In this case, the calculation procedure is changed. The panels are more rigid. If their thickness is 1.5-1.8 cm, the step is taken equal to 0.4 m.With a thickness of 2.2-2.4 cm, the step increases to 0.6 m.The sheets are attached to the logs at three points: in the center and around the edges. Sheets are laid on the logs in such a way that the adjacent panels touch in the middle of the support.

Examples of calculating the lag for a wooden floor
Knowledge of the theory does not always allow you to apply it in practice. In this case, it is worth getting acquainted with an example of calculation for various buildings.
Standard panel house
Here is an example of a calculation for a room measuring 3 × 5 m. The base screed acts as a support. Adjustment by means of clamps is provided. For the device of the subfloor protrudes plywood thickness of 20 m. Decorative coating - laminate.
Guided by the reference data, we take a step of 30 cm. For a span of 3 m, we choose a beam with a section of 150 × 80 mm. The gap between the wall and the extreme lags is 50 mm. The required number of elements is found from the equality 300 × (x-1) + 80 × x + 2 × 50 = 5000. After the performed calculations, you can find that x = 12.1 beams. The found value is rounded to the nearest integer. If the service load is light, 12 beams are sufficient. Otherwise, you can accept 13.

Frame building
In this case, the initial data is the step between the floor beams, equal to 1 m. The rest of the parameters are the same as in the previous example. Using the reference data, it can be established that with a plywood thickness of 20 mm, the logs should be located with a step of 0.3 m. In this case, the beams are at a distance of 1 m from each other. In this case, first, logs are attached to the sides of the beams and aligned. Then bars are placed across the primary logs with a step of 0.3 m.
The length of the primary beams is taken to be equal to the length of the beams - 3 m. Their cross-section should not be less than 200 × 150 mm. For a room 5 m long, the required amount x is found from the equality:
300 × (x-1) + 150x + 2 × 50 = 3000
After solving the equation, you can find x = 5.3 pieces. The value is rounded up to 4 or 5, depending on the expected load. Additionally, a correction is made for increased load, which depends on the operating conditions frame house.

Errors made when calculating the lag for plywood, and their consequences
The typical mistakes that are made when calculating a lag for plywood include too wide a step, insufficient amount of lag, and incorrect section sizes.
The negative consequences of such errors include:
- the appearance of cracks on plywood;
- plywood deflection;
- damage to the decorative coating;
- irregularities on the surface of the topcoat;
- destruction of supporting elements.

How else can you calculate the size and number of elements for installing the floor along the logs
Not everyone is able to perform the calculation on their own. In this case, you can use alternative options. There are various ways to find the required values, each of which deserves attention.
Online calculators and computer programs
Many users turn to online calculators and specialized programs in this case. To calculate the lag parameters, their number and step, you just need to fill in the appropriate cells. The program will give the final value.
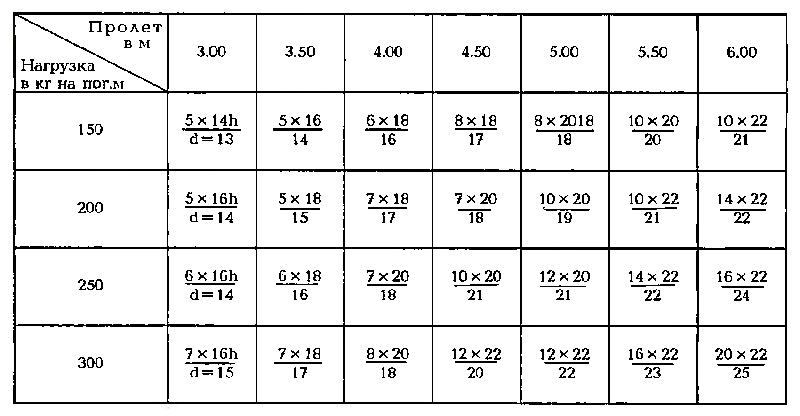
Average tables
There are many reference tables that contain information relevant to users. In them you can find the recommended cross-sectional dimensions depending on the span length. Based on the selected lag parameters, a step is selected between the stacked panels. The obtained values are averaged and do not allow assessing the real load on the supporting elements.
Professional design organizations
To be sure of the correctness of the calculations, it is worth contacting a professional design organization for help. Here the operational load will be taken into account, the possible sizes of the logs and the distance between them will be proposed.
Share in the comments if you have ever had to calculate the lag. Which way did you use?



