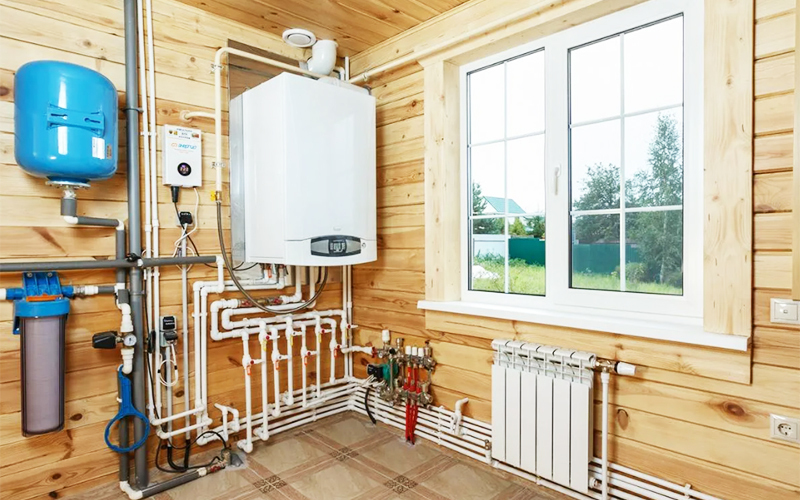
There are several options for heating in the house, but the water circuit is still the most popular. The secret of success lies in the exceptional efficiency and practicality of this choice. Heating systems of this type work in any climatic conditions. And if we consider the varieties of water circuits, then the two-pipe heating system of a private house is the best choice of all.
Read in the article
- 1 Features of dual-circuit heating and the difference from single-circuit
- 2 Varieties of two-pipe circuits
- 2.1 Open and closed heating distribution
- 2.2 Natural and forced circulation of the coolant
- 2.3 Vertical or horizontal layout?
- 2.4 Top and bottom wiring in the heating system
- 3 Advantages and disadvantages of a two-pipe heating system
- 4 Nuances of planning and calculations of two-pipe systems
- 5 Installation of a two-pipe heating system
Features of dual-circuit heating and the difference from single-circuit
First of all, a two-pipe heating system is a closed circuit, along which runs coolant, moving from battery to battery and returning to the boiler, which heats up again content.
Getting into the radiators, the coolant transfers thermal energy to the metal. This energy is replenished by a solid, liquid or gaseous fuel boiler.

The simplest version of the circuit is a single-pipe one, where one channel connects all the radiators, and it turns out that the first one will be the hottest, the second one will no longer heat up to such a temperature - and so on. The last battery in such a circuit will be minimally warmed up. A two-pipe circuit is different in that the supply pipe fits separately to each radiator, allowing they evenly warm up and, accordingly, maintain a stable temperature in all rooms of the house.
Thus, the two-pipe circuit has a supply battery suitable for each radiator, and a "return" that drains the cooled water to the boiler for new heating. It turns out that each radiator receives an individual coolant, heated to the temperature necessary for efficient heating. The result is an optimal thermal balance.
Varieties of two-pipe circuits
At first glance, such a complex heating system as a two-pipe one is not essential for small houses. But it is worthwhile to clearly understand the differences between it and a single-pipe design. For each specific house, its features of layout and area, there may be different recommendations.
Open and closed heating distribution
An expansion tank is present in the design of any heating system. Its task is to compensate for the expansion of the liquid during heating. The volume of the coolant increases with increasing temperature, and the tank acts as an additional container that does not allow the pipes to burst from excessive pressure.
This principle of constructing the circuit leads to the fact that a small part of the coolant evaporates during operation. It is imperative to control the filling level of the expansion tank in order to prevent air from entering the system.
This design is the simplest and is used in most private homes. The disadvantage of this type is that at low room temperatures, the coolant in the open tank quickly loses temperature, and this increases fuel consumption. Well, the need for constant monitoring is another disadvantage.
For an open circuit, only water is used as a heat carrier. All other types of coolants evaporate more actively and can release substances undesirable for humans into the atmosphere.
A closed heating circuit, as you probably already understood, is different in that it also has an expansion tank, but of a closed type. That is, the entire circuit is sealed, has no contact with the atmosphere.
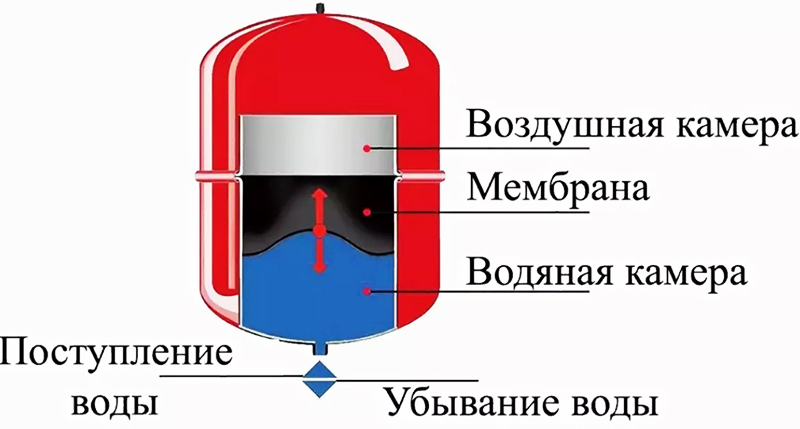
The sealed circuit allows the use of other types of coolant. For example, if you use antifreeze as a coolant, the system will not be afraid of freezing. It is convenient if you solve the problem of heating in the country, which you rarely visit in winter. And so you do not have to drain the contents of the radiators every time before leaving.
Natural and forced circulation of the coolant
The circulation of the coolant in a two-pipe system can be organized according to two principles.
The first is natural circulation due to the physical principle of the expansion of liquids when heated. With an increase in the temperature of the coolant in the boiler, the liquid expands, its density decreases - and according to the laws physics, it rushes up, and cold water, thus following the hot one, in turn falls into boiler. The heated coolant reaches the highest point in the heating system and moves downward by gravity. Thus, the circulation process occurs naturally, without the use of any additional mechanisms. The advantage of such a system is its autonomous operation, not dependent on extraneous energy sources, as well as the absence of risk. airing the system, because the air formed in the pipes during circulation rises and exits through the expansion tank.
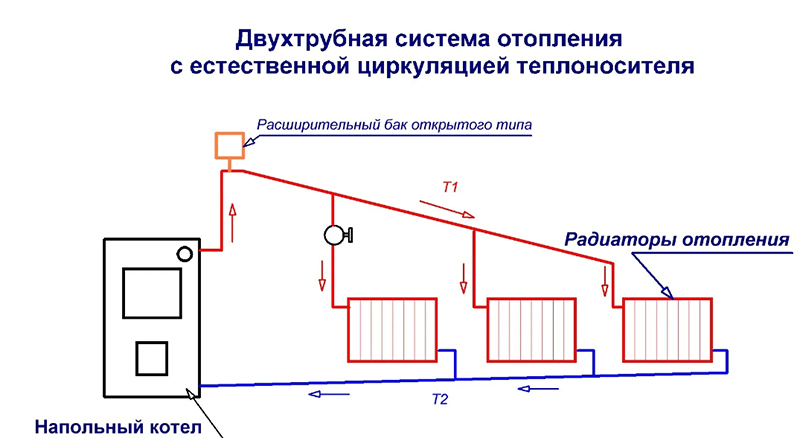
The slope for natural circulation should be at least 2-3 millimeters per linear meter. This design has a large life resource, can be operated for at least half a century. The downside to natural circulation is that it has a rather limited range, so it's not the best idea for large houses.
And many more users do not like that such a system needs to be heated for a long time in order to accelerate the circulation process to an acceptable speed. So its start-up definitely takes more time than in systems with forced circulation.
An interesting observation: a heating system with natural circulation of the coolant is able to self-regulate. If the temperature in the room drops due to external influences, the movement of the coolant becomes faster by itself, since the liquid cools faster in the radiators and moves through the pipes.
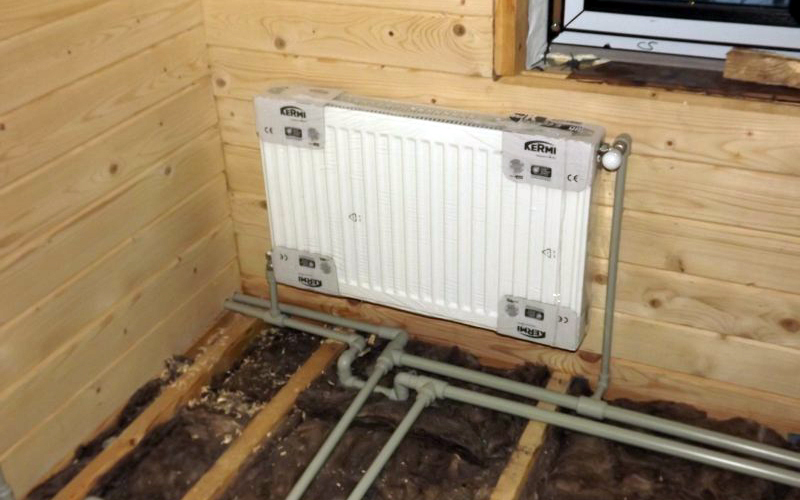

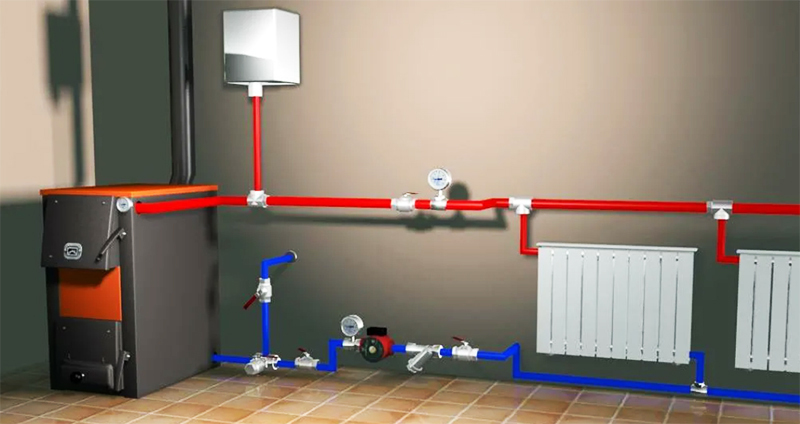
Forced circulation is distinguished by the installation of a pump that automatically accelerates the coolant through the system. Adding this device to the system gives it certain advantages. The circulation speed increases significantly, which allows you to overclock the system and warm up the house much faster, in addition, the batteries receive a coolant with approximately the same temperature, so it is much easier to maintain a microclimate in different rooms, while with natural circulation, radiators located at a greater distance from the boiler are always much colder than those closer to him.
If circulation occurs with the help of a pump, in a two-pipe system it is possible to shut off part of the batteries if necessary. With the second option, this is not possible.
The system with forced circulation can be completely closed, which does not allow the evaporation of the coolant. Among other things, the advantage of this type of heating is simplified installation. That is, it is no longer important to observe the slope, to build a strict scheme for connecting radiators in series - with forced circulation, everything is much simpler. And what is also important - if you are planning to attach more rooms to the house - you can easily include them in the general heating system with forced circulation. All components can be of small diameter - which means that you will significantly save on materials. On the other hand, the operation process will constantly require you to spend on electricity for the pump, and you will be dependent on its availability.

Vertical or horizontal layout?
The horizontal layout is often used in buildings that have a large area, but one floor. The obvious disadvantage of this design is the tendency to form air locks, so Mayevsky cranes are installed in the system without fail. The vertical directions in this option are minimal, and the supply and return can be completely hidden under the floor, which only plays in favor of the aesthetics of the interior. With such a structure, the system is necessarily made with forced circulation.
Note! In a horizontal version of the layout with a passing movement of the coolant, the use of pipes made of polypropylene is undesirable.
The second layout option, vertical, is best suited to two-story buildings. In this case, heating risers are installed, and circuits for each floor are already connected to them. Such a structure does not form air locks, since all the air in the system naturally rushes up, where it exits through the expansion tank at the top of the structure.
The system maintains a high level of pressure, which allows the use of pipes of the same diameter.

Top and bottom wiring in the heating system
It must be admitted that from an aesthetic point of view, pipes under the ceiling are not the best idea. Moreover, part of the thermal energy will go to waste, literally heating the ceiling.
The upper principle of wiring will require a greater consumption of materials for installation, but it guarantees a high circulation rate of the coolant.
Despite the fact that the option with the top wiring is quite practical in terms of organizing a natural circulation in the system, it is still better to place the supply pipes directly above the radiators without violating the aesthetics interior. And besides, if you have made a choice in favor of forced circulation, you will not have any inconvenience in this regard.
The lower wiring of a one-story building provides for the supply and return from the bottom of the battery, the system may include several circuits, including a dead-end one. In this case, you won’t have to start wiring in the attic, and this is already part of the solution with insulation.
The main disadvantage of a circuit with a lower wiring is the risk of air pockets. There is no way to do without Mayevsky cranes for bleeding air.

Advantages and disadvantages of a two-pipe heating system
The advantages of a two-pipe heating system are exceptional operational reliability, invulnerability to emergency freezing, high heat transfer and heating capacity. If necessary, a two-pipe system is not difficult to increase by one or even several rooms. With such a circuit, you will be able to accurately control the temperature in the house, and in all rooms it will be consistently the same.
Nuances of planning and calculations of two-pipe systems
Making a heating system "by eye" is fraught with many troubles, and the main one is being in a freezing house in the middle of winter. Competent calculations will allow you not to spend unnecessary materials, provide for all the nuances and, most importantly, be sure of the result.
The simplest calculation of heating power for the area of \u200b\u200bthe house is as follows:
Q (power) \u003d S (internal cubic capacity of the building) × A (average watts 100-150) × k (power factor within 1.2 or 1.25).
This is the simplest calculation that allows you to more or less rationally calculate the necessary parameters. But it should be noted that for a more detailed calculation, there are other formulas that include such variables, like the height of the ceilings, the features of the building material of the walls, the climatic features of the region, and the like.
The second important parameter that should also be taken into account is the calculation of hydraulics for the system. Properly made measurements in this regard will avoid excessive pressure in the pipes and unbalance of the entire system.
The volume of the coolant is calculated by the formula:
V (volume of coolant) \u003d 13.5 × Q (boiler power).
Heat carrier pipe diameter:
D (pipe cross section) = √354×(0.86×Q (boiler output)):(K (heat carrier tº at the boiler outlet) –Ko (coolant return tº)):V (coolant circulation rate).
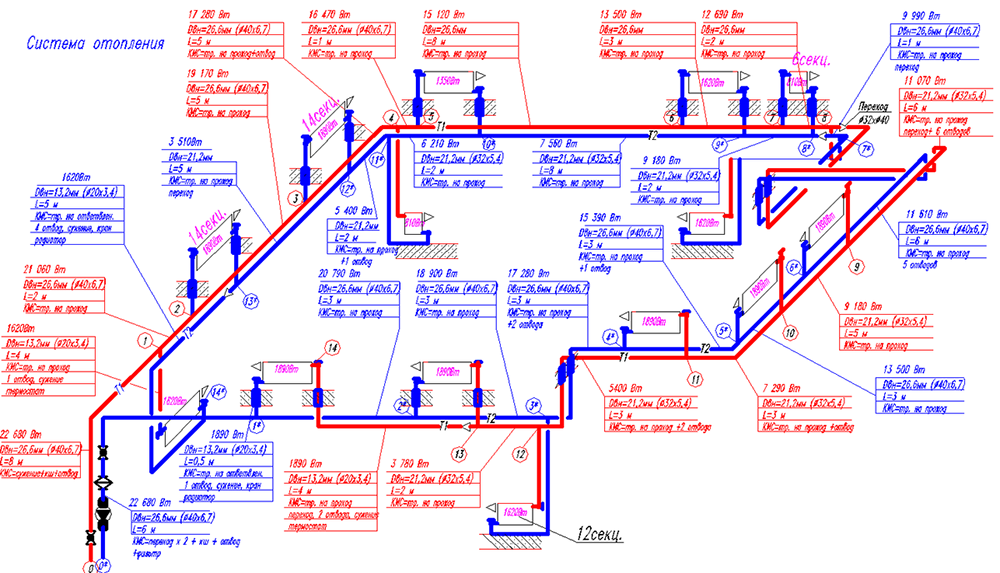
Installation of a two-pipe heating system
Installation of the system starts from the location of the boiler. A central vertical line is installed from it, on top of which an expansion tank is mounted. From this place there is a branching further, at the end of each there is a radiator.
The return pipe is mounted below the boiler. The pump can be installed either on the return line or on the central riser - this does not matter if you have a system with forced circulation.
The do-it-yourself installation algorithm is described in detail in the following video.
What system provides heat in your home? Share your experience in the comments!
The house is much better than the apartment, I'm not surprised that she moved out of town. We actually…
She's lucky. We could not afford to buy an apartment in Moscow. Bought from Terem-pro zag ...
Everything will be if you purchase electrical appliances for 12 volts.
There are 4 panels in the country house and that's enough for everything.
What are these blocks you have so rotten? Never had a problem with gas silicate blocks...
We saved up for a long time, we had to severely limit ourselves in the usual things, until we found out ...
In general, as far as I understand, this is done differently in different regions. Yes, looking at...
I have such a question if I have a central gas pipe that runs right next to the house p ...
Especially with the insulting hint that not new yarn was used in my product, but ...
Hello. It is very unpleasant that you use other people's photos in articles without asking ...
With my own hands, I can't build very well. My wife and I decided to buy a bath from the tower ...
Partly, I liked the interior, I was impressed by the estate, I started to smile, only …
In my opinion, going to the village is too much, if there are no plans to take care of the household. Could…
It looks more like Lerchek bartered furniture, renovations, décor, and clothing. And there h...
When Buryatia was included in the Far Eastern Federal District, housing prices jumped more than 2 times due to this ...
It's a pity we don't have such a program as in the Far East. I had to buy a country ...



