Beam is called a piping layout in centralized heating. It is used, as a rule, in apartment buildings. Radiant heating is also used in multi-storey private mansions and cottages, as well as in commercial buildings.

The device and principle of operation of the radiant heating system
Unlike one-pipe and two-pipe connection schemes, where the radiator batteries are connected in series and form a single pipeline, with a radial heating scheme, each radiator is connected by a separate pair of pipes and they all converge in a collector - a single collector pipelines.
The diagram of a radial heating system implies the presence of an inlet pipe that supplies the coolant, and a return pipe, along which the latter returns back to the boiler.
The radiant heating system is convenient because the pipes are hidden under the floor and do not spoil the interior design with their presence. The collector is recessed in a wall niche. Alternatively, a neat collector cabinet can be mounted for it, which is usually decorated in the color of the finish and looks attractive.
Note! It is important that there are no connecting and especially shut-off fittings in the part of the system hidden from prying eyes. All of them should be located in a cabinet or on a radiator. That is, in places accessible for service.
Like any steam-water heating system, the radial one also begins with a boiler and an expansion tank. For the device, its preference is given to indirect heating boilers, a distinctive feature of which is that that the coolant in them is outside the boiler (in pipes), and the heating medium in the form of steam or water is in the container of the latter. Hence the name of the room in which the water heater is installed - the boiler room.
On a note! Now the term "boiler" has become synonymous with any storage boiler. But it's worth knowing that this is not always technically true.
When installing a beam system, instrumentation is installed on the boiler, but most of them mounted in a manifold, where temperature, water flow and pressure are monitored in each individual ray.
The collector-beam wiring scheme can be single-circuit and double-circuit. A single-circuit heating system means a cycle of water movement from the boiler to the radiator and back along the return line. The two-circuit system, in turn, is a radiator heating combined with hot water supply or radiator heating, working in tandem with the “warm floor” system.
Note! Considering the extensive network of the ray system, consisting of several collectors and a fairly significant number of pipes, connected to them, we can talk about a multi-circuit system, where each collector is a separate circuit.
All of the above makes it mandatory to install hydraulic switches or hydraulic separators, which will protect the boiler and the entire heating complex. They are usually installed at the outlet of the boiler, and in case of multi-circuit assembly - in front of the collectors. A circulation pump also plays an important role in the operation of a heating system with a radial wiring diagram. And this should be taken into account during installation.
In the photo there is a hydraulic arrow designed for several circuits.

How the collector-beam system differs from others
In district heating systems, the following pipe routing schemes are generally accepted:
- One-pipe scheme, nicknamed "Leningrad". This wiring option continues to be used in small private houses with a minimum amount of heated space. Leningradka is appreciated for its ease of installation and minimal material consumption.
- Two-pipe system. It received the name "Tichelman's loop". Its installation is complicated by the presence of doorways for balcony doors and floor-to-ceiling windows. These obstacles force the installation of additional pipes, which increases the consumption of materials.
These systems are assembled with a tee or perimeter connection, which has one serious drawback. The fact is that if any one unit fails, the entire system has to be stopped to carry out repairs, which is especially difficult when it is winter outside the window.
The collector-beam heating system is devoid of the disadvantages inherent in the Tichelman loop and one-pipe systems. Its main difference from one-pipe and two-pipe connection schemes is that each battery has its own line and is not fastened to a neighboring battery. All pipes in the manifold converge like rays, which is obvious from the name.
Key advantages and disadvantages of a radiant heating system
Radiant heating has its own advantages and disadvantages. The advantages include:
- Ease of installation that does not require high qualifications. Any private developer with basic knowledge of plumbing can assemble such a system;
- Reliability. The simpler the installation and the fewer connecting elements in the circuit, the stronger it is. Thus, reliability is another significant advantage of the beam scheme;
- No additional costs when pumping media;
- Easy to maintain. This is another factor that makes the radiant heating system attractive, the scheme of which is quite popular;
- Autonomy of each beam (each individual object). In other words, in order to repair a single section of the heating system, it is not necessary to shut off the entire system. It is enough only to drown out only the link being repaired, while the rest will continue to work. The autonomy with the beam scheme also allows you to control the temperature in each individual link and room.
Control of the flow rate of the heating agent in each individual link. Now each individual consumer can pay only for his own consumption of heat energy and refuse to pay if the supplier does not provide housing with heat in full. This factor is key in choosing a beam system for apartment buildings.
In this case, the disadvantage of the beam system can be called the material consumption of this pipe routing scheme, since a separate pipeline is required for each separate section. However, material costs are quickly offset by energy savings and comfort when using the heating system.
Main structural elements
Like any heating system, the radiant heating scheme begins with the boiler. This is followed by the expansion tank, piping and pump. The device cannot do without instrumentation, which are represented by: thermostats, manometers, water flow meters and other elements. But unlike other systems, a collector appears in the beam connection of pipes, which is why the latter was called the collector-beam.
On a note! Each user chooses a boiler for mounting the beam system depending on the availability of the energy carrier. Solid fuel boilers run on wood, coal and peat. A gas boiler is installed if gas is supplied to the house.
Selection and installation of a circular pump
The radiant heating system stands out from the rest by the available methods of transferring the coolant. There are 2 main ways in total:
- Gravitational, or natural. With this method, water moves due to the density difference between cold and hot liquid. The cold has a higher density, it is heavier, and therefore rushes down. When laying pipes for the organization of natural circulation, it is necessary to take into account the slope for gravity. The possibilities for the free movement of the coolant remain limited, and therefore developers who install radial heating prefer forced circulation.
- Forced movement of water in the radial heating circuit is created through the use of circulation pumps. It should be noted that the pumps significantly expand the potential of the collector system, without limiting the installation of heating devices either in the number or in the distance between the collector and radiators.
When installing natural circulation, the coolant starts to move only when a significant temperature difference is formed in supply and return pipes, which affects the overall air temperature in the heating system and leads to increased consumption of the following sources energy:
- gas, if a gas boiler is installed;
- electricity during the operation of the electric boiler;
- coal or firewood, when using a solid fuel unit.
Forced circulation forces the coolants to move faster, preventing the water from cooling completely. This saves energy.
When installing a system with forced circulation, there are some nuances that you should be aware of:
- In heating systems, pumps for clean water are installed. But they are very sensitive to particulate matter. Therefore, before installing and connecting the hydraulic pump, it is necessary to flush the pipeline system so that no solid particles and dirt remain in it. Also, a filter must be installed in front of the inlet pump to prevent contamination.
- During the installation of the pump, it is important to ensure that the impeller is directed in the direction of the movement of water. If the pump is installed on the supply, then its impeller must direct the coolant towards the radiator; and if the pump is installed on the return, then the movement of water is directed towards the boiler. There is always an arrow on the pump casing that points in the direction of flow.
- Household pumps operate on 220-230V voltage. When installing the device, it is advisable to arrange a separate power supply line for it. Connection is carried out in the presence of 3 wires: zero, phase, ground.
The figure shows the connection diagram of the circulation pump.
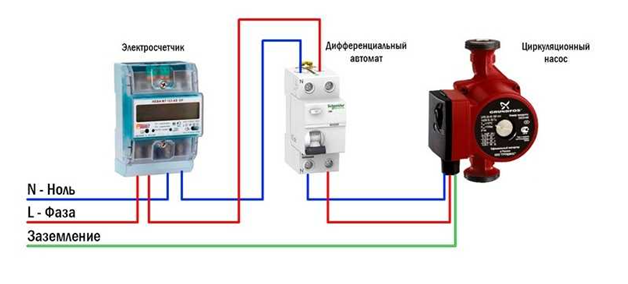
For a private house, it is better to choose a pump with a wet rotor, that is, one in which both the impeller and the rotor are in the water, and the starter and other electrical elements are sealed. With a low, in 50%, efficiency, pumps with a wet rotor are not capricious, they do not require additional maintenance and work for 5-10 years. Such electrical appliances are preferred in private homes, but can be used in other types of buildings as well.
In the picture: the pump is installed in the underfloor heating return.
Dry rotor pumps provide high efficiency - up to 80%. But they require the installation of special filters, additional regular maintenance by specialists.
Such products are used, as a rule, no more than 3-5 years. These pumps are more suitable for multi-storey buildings than for private houses. If only because in the former, scheduled overhaul is relatively often carried out.
On a note! The pump output is selected according to the boiler output. For example, if the boiler has a power of 6 kW, then the pump capacity should be 6 l / min.
Selection and role of a distribution manifold
The collector, which received the name of a comb among specialists, serves as a distribution device for separating the coolant between heat consumers.
This device is a pipe with built-in threaded nozzles, which is why it is called a women's hair accessory.
All pipes from radiators or elements of a water-heated floor are connected to the collector. On the comb, thermostatic, shut-off and control, measuring instruments are installed, which in in general, they control the flow rate of the coolant while observing the optimal air temperature in the heated premises. Air extractors from each circuit are also built in here.
In multi-storey and apartment buildings, collectors are installed on each floor. To give more aesthetics, as well as to protect the equipment, special cabinets have been developed for distribution systems. The best option is when special niches for such cabinets are provided in the architecture of the building. But their installation is possible outside, and in any place suitable for this, so even if they are absent in the project, installation will not be a problem.
On a note! Collector cabinets, as a rule, have compact dimensions, they do not take up extra space, differ in functionality and practicality.
When choosing a collector, it is taken into account:
- The material from which it is made. For a heating system, it is better to buy collectors made of stainless steel or brass.
- The number of consumers and their correspondence to the number of branch pipes. It is allowed to install a collector with one extra element, no more.
- Comb type. There are radiator and clamping ones. The latter are also used in heating systems less often than the former.
If the system has identical radiators with the same number of fins, a radiator manifold will do. On the branch pipes of such combs, ball valves are installed that work for opening and closing. This is the simplest type of combs.
Clamping combs are mounted if heating devices in the radiator system differ in type, volume of consumed heat carrier and power. Such combs differ from radiator combs by the presence of adjusting screws that are installed on top or on the side.
Note! The more the adjusting screw is tightened (closed), the less coolant enters the circuit. The heat supply is balanced with the adjusting screws. For a more even distribution of the coolant between the batteries and the underfloor heating, the supply of the coolant is reduced precisely to the pipes leading to the floor heating.
It will be appropriate to install a sump with a filter mesh in front of the collector. This device will increase the length of the comb and, thereby, help the coolant to be distributed between the nozzles more evenly. But the most important thing is that this element will not allow dirt to get into the pipes, as well as into the collector.
On a note! Another significant advantage of the mud collector is the ease of disassembly before flushing the filter mesh, which almost everyone can do.
The picture shows a collector-beam heating system with inlet and outlet combs.

Beam wiring diagram
Installation of a radiant heating system is available to anyone who has locksmith skills and knows how to hold tools in their hands. For work you will need:
- adjustable or gas wrench;
- electric drill with victorious drills;
- pipe cutter for plastic and metal-plastic pipes;
- manual or hydraulic pipe bender;
- a calibrator for preparing pipes for putting on fittings and connecting to each other;
- soldering iron for plastic pipes;
- Bulgarian.
Preparatory work
Before starting the installation of a radiant heating system, it is necessary to create its project, which indicates location of radiator batteries, their number, as well as the number of blocks in each battery, taking into account their heat transfer.
Even during the design process, you should calculate the number of pipes supplied to the radiators, think over the location of the collectors, as well as to plan the route of laying the networks, and only then can you proceed to calculation of their length.
On a note! On the eve of installation, the most suitable collectors have to be selected. Manufacturers produce combs with the number of nozzles from 2 to 12. Combs with the maximum number of nozzles are used, as a rule, in multi-storey buildings.
Depending on the size of the house and the number of radiators, the power and volume of the boiler are calculated. Then you have to calculate the number of fittings and valves. Do not forget that you will also need to buy valves to bleed air from the system.
Mounting
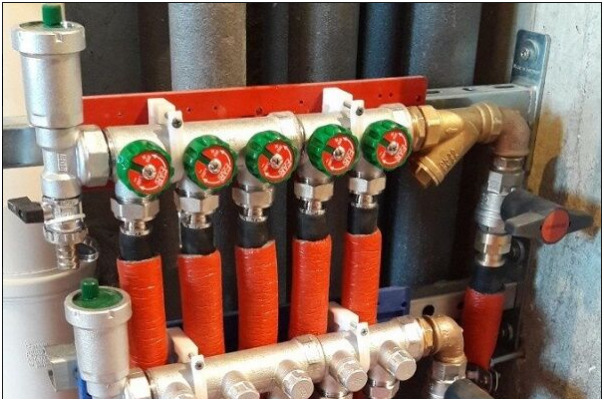
Installation of radiant heating in an apartment or in a private house, as a rule, begins with radiator batteries. Using a laser level, the height of the radiators is marked and, in accordance with the selected indicator, holes are drilled for their fastening. The batteries are then hung and aligned. Moreover, the latter is performed both in height and in distance from the wall. Simultaneously with the batteries, a collector is attached, consisting of two combs: for hot water and for return. Thus, if 6 radiators are installed in the room, then two combs with 6 pipes each will be required.
In the picture: a collector with measuring instruments.

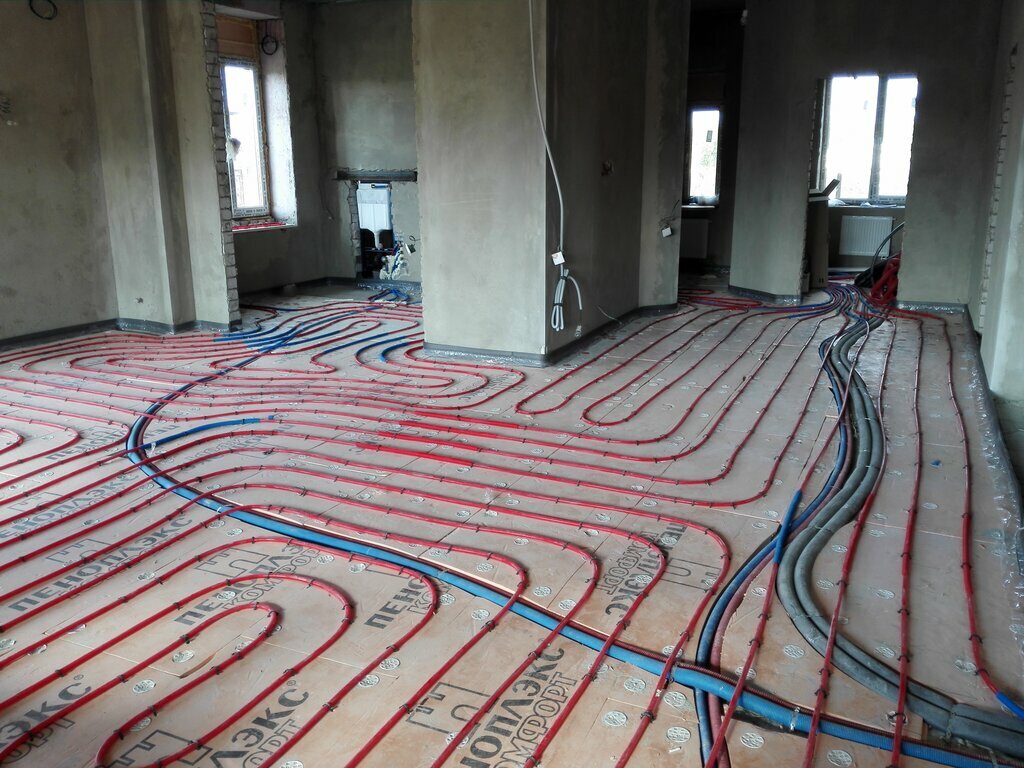
The next stage is pipes. It is recommended to wear corrugated sleeves of a slightly larger diameter on these products before fastening in order to reduce heat loss. For installation, they are laid by guides and only then the pipes themselves are laid.
Note! Guides are special devices with cells into which several pipes are inserted. The cells, fixing them, prevent displacement, they form a direction for their rotation at the desired angle and in the required direction.
The pipes can also be fixed with a special fixing tape, which is attached to the floor with brackets or self-tapping screws.
Remember: pipes that are laid from the collector to the radiator must be solid, without connections. This can be achieved by buying them in linear meters in tubes and subsequently cutting them along the length from the collector to the radiator. The desire to save money by connecting the pipes to each other with fittings will eventually result in a leak and the need to open the floor.
When all the pipes have been laid, they are adjusted to be connected to the radiators. At the same time, connecting fittings are mounted to the batteries, having a square at the end, to which the supplied pipes are finally connected. Each battery has two ends: the first with the coolant and the second for the reverse flow.
When the pipes are fitted and connected, fasteners are screwed to the floor, fixing them completely. This is followed by the connection of pipes to the manifold. In the assembly process, when connecting fittings, tow is used as a sealant, as the material most resistant to temperature extremes.
Radiation system and warm floor
Steam-water heat-insulated floor perfectly integrates into the radial connection system. This design of the heating system is of particular importance on the ground floor of any building, whether it has two or 20 floors. By installing a “warm floor”, you can increase the heating efficiency by 20-25%, so if you get such an idea, then you shouldn't give it up. Moreover, the installation process is not as complicated as it might seem at first glance.
Well, we have prepared for you some practical tips that will come in handy when installing a warm floor built into a radiant heating:
- A thermo mixer with American nuts is installed on the pipe connecting the radiator comb with the underfloor heating comb. This device will balance the heat energy between the radiators and the underfloor heating. Thermo mixer is a consumable device that requires systematic cleaning, repair or replacement. And to remove it, it will be enough to unscrew the American women.
- Before putting a warm floor on the screed, the concrete coating is insulated with an insulating layer of foil-clad polyethylene. A reinforcing mesh is laid on top of the insulation. It will serve as a base when pouring the screed, and pipes of a water-heated floor are attached to it with wire.
- For the installation of the system, a reinforced-plastic or plastic cross-linked polyethylene pipe with a diameter of about 15 mm is used. These pipes are preferred because, firstly, they keep the temperature well, and secondly, they are flexible and easily bend.
- Some masters do not recommend using stainless steel and polypropylene pipes in a warm floor. The latter are not resistant to high temperatures, they are characterized by increased fragility. They have a high coefficient of expansion and, at the same time, they are not as flexible as XLPE or reinforced plastic, which are sold rolled into tubes. In addition, the operation of polypropylene is allowed at temperatures not exceeding 90 ° C.
Features of the installation of the system for wooden houses
In a wooden house, both the subfloor and the finish floor are made of wood. And this has its own design features when installing a heating system. When wiring, the pipes lie on the beams and logs across, and so that in the process of laying the boards of the main floor, they did not interfere, did not protrude and did not pinch, in the logs, holes should be drilled or milled for pipes. These holes should be 3-5 mm larger than the diameter of the pipe itself, given that its body expands when heated.
The pipes should be fastened to the planks with clamps. But before laying them, it is necessary to cover the steam and waterproofing material, and lay thermal insulation on top of it.
So that during the repair of the heating system it is not necessary to open the floor, fittings and connecting fittings should not be under it. Installation should be carried out in such a way that all fasteners, valves and other fittings are above the floor covering.
In the photo: Radiation system and warm floor

Expert recommendations: 10 tips for those who decide to install a radiant heating system themselves
Heating experts recommend listening to the following tips:
- During installation, thermostats and thermostats should be installed at some distance from heat sources so that their readings are not distorted;
- Before starting the installation of the circulation pump, it is recommended to flush the system so that no solid impurities remain in it that negatively affect the rotor and impeller;
- If it is assumed that the pump will be installed on a branch with hot water, then when purchasing a unit, you should pay attention to the temperature regime of operation. A pump that is not designed to work with hot temperatures is installed in the return;
- It is advisable to mount an air vent together with the pump.
- Before the control and subsequent starts of the pump, the system must be filled with water. Do not turn on the device dry.
- It is advisable to cover the subfloor on which the pipelines of the radiation system are laid with a heat-insulating film, and put on corrugated sleeves on the pipes. To make it easier to distinguish between supply pipes and return pipes, two-color sleeves should be chosen. For heating, manufacturers produce red and blue. They should not fit tightly. There should be a free space of 2-3 mm between the sleeve and the pipe, since hot pipes expand from heat.
- If a house, even a private one, is built on two floors or it just has an attic, a separate collector is installed on each floor. In this case, the riser is located in the corner closest to the place where the collectors are located. In multi-storey buildings, for ease of installation, the collectors are usually located one above the other and each, respectively, on its own floor.
- According to some experts, there is no need to install pressure gauges or thermometers on the manifold. Thermostats are installed in a heated room, they are located on the boilers and the meter. By the way, the main indications are taken from the latter. Manifold gauges are an unnecessary luxury.
- In stone and, especially, in panel houses, heating will be economical and sufficiently effective if we first insulate the outer walls and floor.
- You should not skimp on steel fittings that connect the radiator to the underfloor heating. The tube of L-shaped products is stronger than heating pipes, so it will exclude breakage in the connection.
User reviews
Novosel Misha:
“I heard from experts that the beam is an indestructible system, but somehow I didn't really believe it until I installed it myself in my house. I planned it myself, and, to be honest, not really going into calculations and engineering subtleties.
But just in case, I installed a regulating valve for each battery. Adjusted once on first start. The batteries heat up evenly. I did not make any adjustments, and I suppose I will not. The system is simple and reliable. It is maintainable. Each battery, if necessary, can be repaired without shutting down the entire system. Which is also a very big plus of the ray ”.
Plumber Peter:
The pluses of beam mounting, in my opinion, include:
- comparative ease of design;
- accuracy in balancing, in other words, in setting up equipment;
- smaller, in comparison with other schemes, the number of connected elements.
Well, and of course, the ability to measure, control each beam separately, and also turn them off at one point. The latter outweighs all the advantages and even disadvantages.
The disadvantage of the system is the impossibility of open installation. Everything is hidden in the floors or in the niches of the wall. It is, of course, beautiful, aesthetically pleasing, but not always convenient. And one more drawback of the system is its overpriced. Although more pipes and fittings are used, due to their smaller diameter, their price is cheaper, which partly compensates for the increased consumption of materials. For example, if pipes and fittings of 20-25 mm are used in the tee wiring, then in the radiant heating scheme their size is 15-20 mm ”.


