Usually people do not notice what comfort rests on. The apartments have water supply, sewerage, hot and cold water, heating and air conditioning. The summer cottages have swimming pools and lawns. All this is impossible without the use of special equipment - pumps.
There are fountains in the streets and parks. Gasoline is poured into car tanks at gas stations. Storm water from roads and sidewalks is regularly pumped out. These are just examples of the use of pumping units. It is interesting to find out what the pump consists of and how it works.
Content
- 1 What is a pump and what is it for
- 2 Device, parameters and characteristics
- 3 Types of pumps and their classification
- 3.1 By areas of application
- 3.2 By the principle of action
- 3.2.1 Volumetric
- 3.2.2 Dynamic
- 3.3 By implementation
- 3.4 By type of pumped medium
- 3.5 Industrial plants
What is a pump and what is it for
It is a machine that converts mechanical drive power into hydraulic fluid power. Thanks to this, its flow is carried out. The machine pumps liquid, moves it to design heights and specified directions.

Device, parameters and characteristics
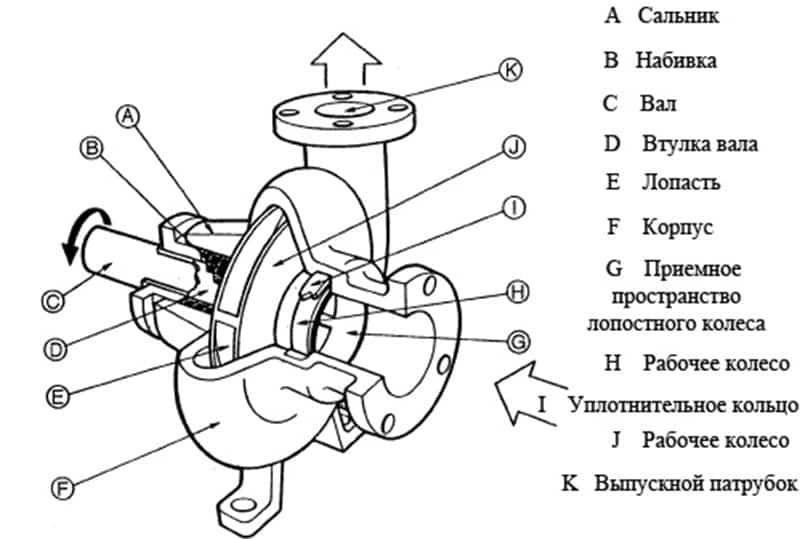
As an example, we will analyze the device of the simplest water pump. It includes a housing with an inlet and outlet pipe. The rotor is inside and is a shaft with an impeller mounted on it.
The shaft rotates from the drive mechanism. The wheel moves water from the inlet (suction) branch to the outlet (pressure). Bearings support the shaft in the housing and facilitate rotation. The seals prevent water from leaking out of the housing.
The main parameters of the pumps:
- consumption (feed);
- pressure;
- engine power.
Consumption - the volume of the pumped medium per unit of time. The pressure is measured at the discharge port. An additional parameter is the suction depth.
The main characteristics of the pumps are the dependences between the main parameters for different operating modes. Pressure characteristic - the relationship between the pressure in the discharge pipe and the flow rate (supply). The larger one parameter, the smaller the other. This characteristic is used to determine the operating modes.
Types of pumps and their classification
The variety of types of pumps and their names helps to understand the classification system according to the main features (according to the principle of operation pump and structural device, according to the properties of the pumped medium and according to the purpose) and auxiliary (according to the fields of application and species). Some signs have additional internal structure.
Interesting on the site:
What is a water cooler: principle of operation and description of the device
What is a projection TV and how does it work
What is a bactericidal irradiator-recirculator, how to use it
By areas of application
What are the pumps on this basis? All varieties are divided into household and industrial. Household ones are intended for pumping water in the household: for watering summer cottages from wells and wells, in household appliances, for supplying and pumping water.
The rest are used in all spheres of the economy: in industry and energy, transport, utilities and agriculture. They are irreplaceable in the mining and petrochemical industries. They are used in the Ministry of Emergency Situations and the armed forces.
By the principle of action
According to the principle of operation, pumps are displacement and dynamic.
Volumetric
Volumetric units can be reciprocating or rotary. Reciprocating ones move the medium as a result of the movement of the piston or membrane along the axis for suction and displacement of liquid from the working chamber. The most common of them are piston.
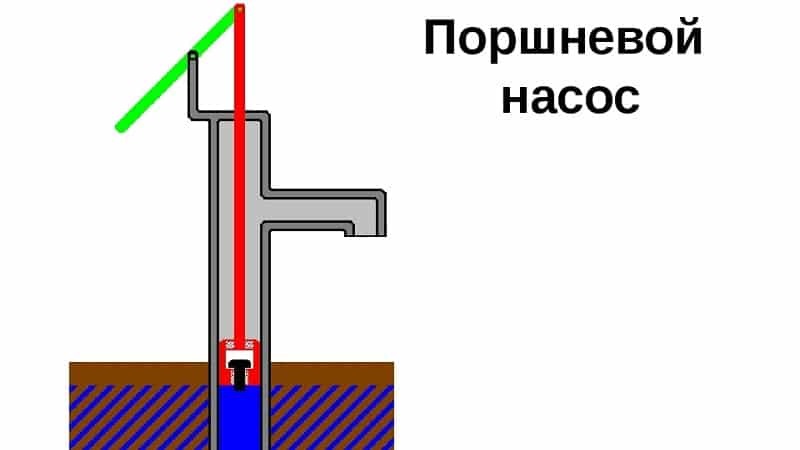
Piston pumps are subdivided according to the types of displacers and drives:
- on pumps of one-way or two-way action (according to the way of action of the piston);
- horizontal and vertical (according to the position of the piston and cylinder);
- Disc or plunger (in the form of a piston);
- electric and steam (by type of drive).
Important! Due to vibration during operation, piston pumps are installed on the foundation, low-power - on the frame.
The advantages of diaphragm pumps are small dimensions and versatility. They are capable of pumping viscous liquids and mixtures with solids. The disadvantage is the rapid wear of the membranes.
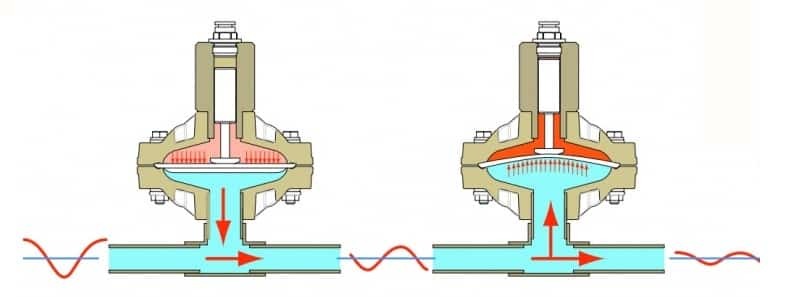
Membrane or diaphragm mechanisms differ in the type of membranes and their number, the number of working chambers and the type of drive:
| Sign | Views |
| Diaphragm design | Flat, molded or structured |
| Number of membranes | One or two |
| Number of working chambers | One or two |
| type of drive | Mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic or electrical |
In rotor mechanisms, rotating rotors form cavities: suction and pressure. The liquid is pushed from one cavity to another. The rotor moves it from the housing inlet to the outlet. This type produces a more uniform feed.
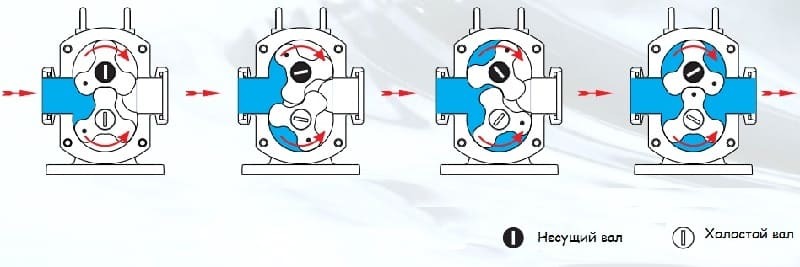
The simple design ensures long service life. They are divided into types according to the design of the rotor - the working body: gear, screw, plate, rotary, roller.
Dynamic
In dynamic aggregates, the flow interacts with a rotating working body and receives an increase in energy. There are two types - bladed and vortex. The impeller has a wheel with installed blades. The fluid moves under the influence of the paddles. In the vortex, there is an exchange of energy of the main flow in the channel of the housing and the secondary in the impeller.
Vane mechanisms in the direction of flow in the impeller are divided into centrifugal (radial, diagonal) and axial. The types of these units differ in the location of the axis, supports, inputs and their number:
| Constructive feature | Name |
| The location of the axis of rotation of the rotor | Horizontal, vertical and tilted axis |
| Location of impellers | Console or monoblock |
| Supports outside the body or inside | Outriggers and internal |
| Approach in relation to the axis | Side entry, axial or double-sided |
| Number of working bodies | Single stage, two stage and multi stage |
| Number of taps when feeding | Single-stream or double-stream |
| Location of connectors to axis | End (sectional) and axially split |
| Body types | Double body or with protective housing |
| Under the liquid level | Submersible or semi-submersible |
| Contact of the pumped liquid with the external environment is excluded | Sealed |
| On the foundation | Stationary |
| Bends | With volute, annular and guide vanes |
| Rotating the blades | Fixed blades or rotary |
Reference. Centrifugal pumps are the most common.
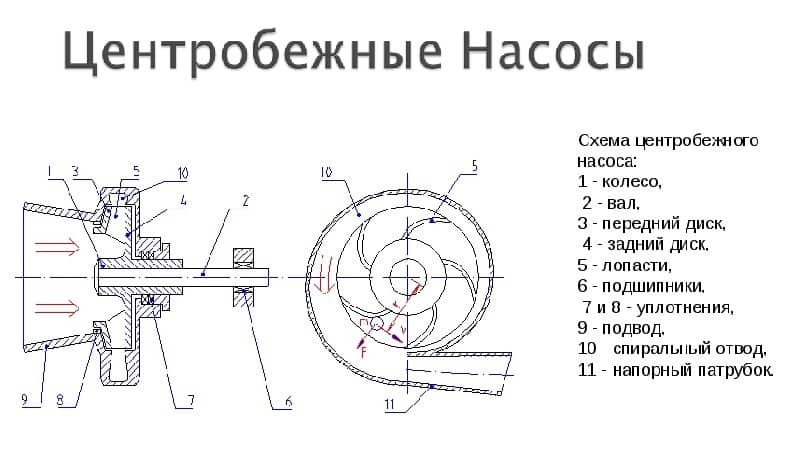
By implementation
According to the method of implementation, there are mechanical, magnetic discharge, jet, sorption and cryogenic. Magnetic discharge vacuum devices are designed for pumping gas mixtures. Jetting mechanisms have no moving parts. Sorption adsorb steam and gas from volumes. Cryogenic ones are installed in vacuum installations during the metallization process to pump out excess gases.
By type of pumped medium
The pumps differ from each other and in the composition of the pumped media. This can be water for irrigation from a pond in the country or hydrochloric acid at a metallurgical plant, concrete solution in construction and chocolate at a confectionery factory. Therefore, before choosing a design and materials used in the manufacture, information is needed on the chemical and physical properties of the pumped medium.
Reference. The finding of solids and their size, combustibility, toxicity, chemical activity, the presence of gases, and viscosity are taken into account.
Based on these criteria, six types of environments have been identified, with which they work:
- clean and slightly contaminated neutral liquids;
- contaminated liquids and suspensions;
- slightly gassed liquids;
- gas-liquid mixtures;
- corrosive and radioactive liquids;
- liquid metals.
Industrial plants
The same type of equipment can be used in different industries and technological processes. Pumps are general industrial, artesian, power, fecal, for the chemical industry (made of stainless steel). General industrial devices are used for pumping water and chemically inactive and non-aggressive liquids. Energy includes nutrient and condensate, oil and circulation.
The most common purpose is to pump water. Types of pumps for water - centrifugal, circulating, artesian, submersible, borehole, vortex, surface. Both single-stage and multi-stage are used. The devices are used for clean and polluted water.
There are many factors to consider when choosing a pump:
- purpose and place of use;
- dimensions of the device and method of operation;
- engine's type.
All units are marked for identification. They are made up of numbers and letters. They determine the type and parameters of the mechanism. You can immediately select it according to the specified technical characteristics, then the operation will be long and reliable.
Read also:
What is an airfryer and how does it work
What is a Solo Microwave Oven